VSCode文件配置
c_cpp_properties.json
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"compilerPath": "D:/mingw64/bin/g++.exe", //这里改成自己的路径
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
// 这里添加自己的OpenCV路径
"D:/mingw64/include",
"D:/OpenCV/opencv_build_cmake/install/include",
"D:/OpenCV/opencv_build_cmake/install/include/opencv2"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "clang-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
launch.json
// https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/launch-json-reference
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch", // 配置名称,将会在启动配置的下拉菜单中显示
"type": "cppdbg", // 配置类型,cppdbg对应cpptools提供的调试功能;可以认为此处只能是cppdbg
"request": "launch", // 请求配置类型,可以为launch(启动)或attach(附加)
"program": "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", // 将要进行调试的程序的路径
"args": [], // 程序调试时传递给程序的命令行参数,一般设为空即可
"stopAtEntry": false, // 设为true时程序将暂停在程序入口处,相当于在main上打断点
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", // 调试程序时的工作目录,此为工作区文件夹;改成${fileDirname}可变为文件所在目录
"environment": [], // 环境变量
"externalConsole": true, // 使用单独的cmd窗口,与其它IDE一致;为false时使用内置终端
"internalConsoleOptions": "neverOpen", // 如果不设为neverOpen,调试时会跳到“调试控制台”选项卡,你应该不需要对gdb手动输命令吧?
"MIMode": "gdb", // 指定连接的调试器,可以为gdb或lldb。
"miDebuggerPath": "D:/mingw64/bin/gdb.exe", // 调试器路径,Windows下后缀不能省略,Linux下则不要
"setupCommands": [
{ // 模板自带,好像可以更好地显示STL容器的内容,具体作用自行Google
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": false
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "Compile" // 调试会话开始前执行的任务,一般为编译程序。与tasks.json的label相对应
}]
}
tasks.json
// https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/tasks
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Compile", // 任务名称,与launch.json的preLaunchTask相对应
"command": "D:/mingw64/bin/g++.exe", // 要使用的编译器,C++用g++
"args": [
"${file}",//当前文件名
"-o", // 指定输出文件名,不加该参数则默认输出a.exe,Linux下默认a.out
"${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"-g", // 生成和调试有关的信息
"-m64", // 不知为何有时会生成16位应用而无法运行,加上此条可强制生成64位的
"-Wall", // 开启额外警告
"-static-libgcc", // 静态链接libgcc,一般都会加上
"-finput-charset=UTF-8",
"-fexec-charset=GBK", // 生成的程序使用GBK编码,不加这条会导致Win下输出中文乱码;繁体系统改成BIG5
"-std=c++17", // 要用的语言标准,根据自己的需要修改。c++可用c++14
// 扩展参数
// -I 头文件目录
// -L 库文件目录
// -l 库文件
// 这里换成自己的文件路径
"-I", "D:/OpenCV/opencv_build_cmake/install/include",
"-I", "D:/OpenCV/opencv_build_cmake/install/include/opencv2",
"-L", "D:/OpenCV/opencv_build_cmake/install/x64/mingw/lib",
"-l", "libopencv_calib3d420",
"-l", "libopencv_core420",
"-l", "libopencv_dnn420",
"-l", "libopencv_features2d420",
"-l", "libopencv_flann420",
"-l", "libopencv_highgui420",
"-l", "libopencv_imgcodecs420",
"-l", "libopencv_imgproc420",
"-l", "libopencv_ml420",
"-l", "libopencv_objdetect420",
"-l", "libopencv_photo420",
"-l", "libopencv_stitching420",
"-l", "libopencv_video420",
"-l", "libopencv_videoio420",
"-l", "opencv_core420",
"-l", "opencv_imgproc420",
"-l", "opencv_imgcodecs420",
"-l", "opencv_video420",
"-l", "opencv_ml420",
"-l", "opencv_highgui420",
"-l", "opencv_objdetect420",
"-l", "opencv_flann420",
"-l", "opencv_imgcodecs420",
"-l", "opencv_photo420",
"-l", "opencv_videoio420",
// 中文编码
// "-finput-charset=GBK"
], // 编译的命令,其实相当于VSC帮你在终端中输了这些东西
"type": "process", // process是把预定义变量和转义解析后直接全部传给command;shell相当于先打开shell再输入命令,所以args还会经过shell再解析一遍
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true // 不为true时ctrl shift B就要手动选择了
},
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "always", // 执行任务时是否跳转到终端面板,可以为always,silent,never。具体参见VSC的文档
"focus": false, // 设为true后可以使执行task时焦点聚集在终端,但对编译C/C++来说,设为true没有意义
"panel": "shared" // 不同的文件的编译信息共享一个终端面板
},
"problemMatcher":"$gcc" // 捕捉编译时终端里的报错信息到问题面板中,修改代码后需要重新编译才会再次触发
// 本来有Lint,再开problemMatcher就有双重报错,但MinGW的Lint效果实在太差了;用Clang可以注释掉
}],
}
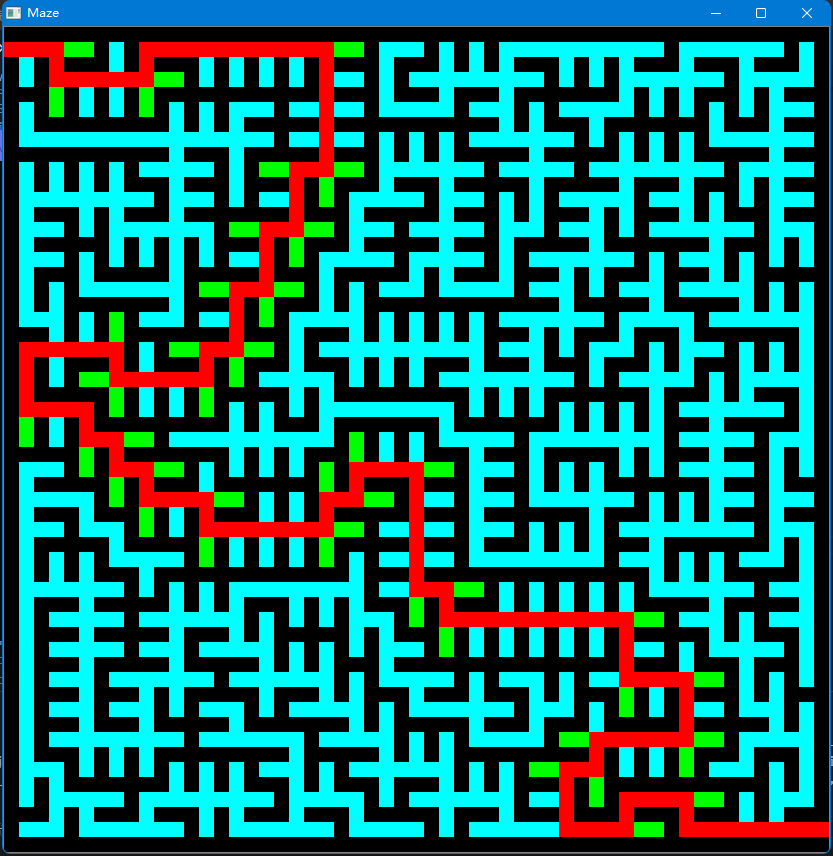
迷宫算法
// Peter Pan
// 21-10-25
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<sys/timeb.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#define IN_MAXSIZE 100
#define INCREASE 10
#define SElemType Single_Point
#define FALSE 0
#define TURE 1
#define a 0 //a表示路
#define b 1 //b表示墙
using std::random_shuffle;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct
{
int x; //行坐标
int y; //列坐标
int direction = 1; //方向
}SElemType;
typedef struct
{
SElemType *base;
SElemType *top;
int stacksize;
}SqStack;
const int n = 181;
const int k = n / 2;
const int N = k * k;
// 迷宫的大小 n * n
int Init_Stack(SqStack *);
int Push(SqStack *,SElemType);
int Pop(SqStack *,SElemType *);
int* randperm(int limit);
void DFSmaze(SElemType [],int [][n],int [][k]);
void PrintMaze(int maze[][n]);
void draw(int x,int y,int flag);
bool MazePath(int maze[][n], SElemType start, SElemType end);
int Pass(SElemType pos);
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S);
void NextPos(SElemType* curpos, int direction);
void MakePrint(SElemType e, int print);
void PrintPath(SqStack *);
const int limit = 4;
const int node_size = 4;
const int sleep_time = 5;
const int wait_key = 1;
int* choices;
int maze[n][n];
struct timeb seed;
// 长度 宽度 CV通道数
Mat mat(node_size * n, node_size * n, CV_8UC3);
int main()
{
ftime(&seed);
srand(seed.time * 1000 + seed.millitm);
choices = (int*)malloc(limit * sizeof(int));
choices = randperm(limit);
int i,j;
int smaze[k][k];
// 结构体数组
SElemType r[(k)*(k)];
// 把所有点都先初始化为墙。
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
maze[i][j] = b;
}
// 先使得横坐标和纵坐标都为偶数的变为路。
for(i=1;i<n-1;i=i+2)
for(j=1;j<n-1;j=j+2)
{
maze[i][j] = a;
}
// 定义起始点和结束点。
maze[1][0]=a;
maze[n-2][n-1]=a;
// 存储结构体数组的横坐标和纵坐标。
for(i=0;i<k*k;i++) //结构体数组赋初值,索引从零开始
{
r[i].x = i/k;
r[i].y = i%k;
}
// 数组中所有的初值全部置为FALSE,表示这些位置都没有被访问。
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
for(j=0;j<k;j++)
smaze[i][j] = FALSE;
// DFS首先访问的节点。
smaze[0][0] = TURE; // 初始节点
DFSmaze(r,maze,smaze);
PrintMaze(maze); // 打印生成迷宫
namedWindow("Maze");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (maze[i][j] == 1)
{
draw(i, j, 1);
}
else if(maze[i][j] == 0)
{
draw(i, j, 2);
}
}
}
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(1000);
printf("Please enter 0 to continue.\n");
SElemType start, end;
start.x = 1; start.y = 0;
end.x = n - 2; end.y = n - 1;
MazePath(maze, start, end);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void PrintPath(SqStack * s) {
int count = 0;
while (s->base < s->top)
{
printf("(%d, %d)-->", s->base->x, s->base->y);
count++; s->base++;
if (count % 8 == 0)
printf("\n");
}
}
void PrintMaze(int maze[][n]) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) // 打印生成迷宫
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%d ",maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int Init_Stack(SqStack *t) //初始栈
{
t->base = (SElemType *)malloc(IN_MAXSIZE*sizeof(SElemType));
if(!(t->base))
return 0;
t->top = t->base;
t->stacksize = IN_MAXSIZE;
return 1;
}
int Push(SqStack *t,SElemType e) //入栈
{
if(t->top-t->base>=t->stacksize)
{
t->base = (SElemType *)realloc(t->base,(t->stacksize+INCREASE)*sizeof(SElemType));
if(!t->base)
return 0;
t->top = t->base + t->stacksize;
t->stacksize += INCREASE;
}
*(t->top++) = e;
return 1;
}
int Pop(SqStack *t,SElemType *e) //出栈
{
if(t->top==t->base)
return 0;
*e = *(--t->top);
return 1;
}
/*
循环弹栈,弹出一个,则将其二维数组中的FALSE改为TURE表示该元素已经被访问了。
然后寻找其上下左右没有被访问的元素,找到一个,则将夹在两个蓝色圈中的墙打破,使其变成路,然后找到的未访问的元素入栈。
*/
void DFSmaze(SElemType r[N],int maze[n][n],int smaze[k][k]) //深度优先算法
{
SElemType e; // 结构体变量e
SqStack s; // 栈里面的存储的为结构体
if(Init_Stack(&s)==1) // 初始栈
printf("OK\n");
else
printf("Fail\n");
Push(&s,r[0]); //压栈r[0]
printf("initializeing maze......\n");
while(Pop(&s,&e)) //栈不空时,进行循环
{
choices = randperm(limit);
for(int i=0;i<limit;i++) {
switch(choices[i]) {
//0,1,2,3分别对应上右下左
case 0: {
// 点不能为外墙并且该结点未被访问过
if(e.x - 1 >= 0 && smaze[e.x-1][e.y]!=TURE) // 上
{
// 该节点的状态变成访问过。
smaze[e.x-1][e.y] = TURE;
maze[2*e.x][2*e.y+1] = a; //打墙
// 这里面r是一个一维结构体数组,每个结构分别存储X坐标和Y坐标。
Push(&s,r[(e.x-1)*k+e.y]);
}
break;
}
case 1: {
if(e.y + 1 < k && smaze[e.x][e.y+1]!=TURE) // 右
{
smaze[e.x][e.y+1] = TURE;
maze[2*e.x+1][2*(e.y+1)] = a;
Push(&s,r[(e.x)*k+e.y+1]);
}
break;
}
case 2: {
if(e.x + 1 < k && smaze[e.x+1][e.y]!=TURE) // 下
{
smaze[e.x+1][e.y] = TURE;
maze[2*(e.x+1)][2*e.y+1] = a;
Push(&s,r[(e.x+1)*k+e.y]);
}
break;
}
case 3: {
if(e.y - 1 >= 0 && smaze[e.x][e.y-1]!=TURE) // 左
{
smaze[e.x][e.y-1] = TURE;
maze[2*e.x+1][2*e.y] = a;
Push(&s,r[(e.x)*k+e.y-1]);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
}
int* randperm(int limit)
{
Sleep(sleep_time);
ftime(&seed);
srand(seed.time * 1000 + seed.millitm);
int* numbers;
numbers = (int*)malloc(limit * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
numbers[i] = i;
random_shuffle(numbers, numbers + limit);
return numbers;
}
void draw(int x,int y,int flag)
{
int red, green, black;
if (flag == 1)
{
red = 0, green = 0, black = 0;
}
else if (flag == 2)
{
red = 0, green = 255, black = 255;
}
else if (flag == 3)
{
red = 255, green = 0, black = 0;
}
else if (flag == 4)
{
red = 0, green = 255, black = 0;
}
// 每个点像素为50?50
for (int i = x * node_size; i < x * node_size + node_size; i++)
{
for (int j = y * node_size; j < y * node_size + node_size; j++)
{
mat.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = black;
mat.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = green;
mat.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = red;
}
}
}
bool MazePath(int maze[][n], SElemType start, SElemType end)
{
SqStack S;
// SElemType* e;
Init_Stack(&S); // 初始栈
SElemType curpos = start;
// 初始点变为红色
draw(start.x, start.y, 3);
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(wait_key);
Push(&S, start);
int direction;
int curstep = 1;
int temp_direction;
do {
if(Pass(curpos)) {
if(curpos.x == end.x && curpos.y == end.y) {
PrintPath(&S);
return true;
}
// 加入当前道路
MakePrint(curpos, 2);
NextPos(&curpos, curpos.direction);
// 如果路不通就往反方向走
temp_direction = (curpos.direction + 2) % 4;
if(maze[curpos.x][curpos.y] != 0) {
NextPos(&curpos, temp_direction);
curpos.direction = curpos.direction % 4 + 1;
continue;
}
Push(&S, curpos);
draw(curpos.x, curpos.y, 3);
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(wait_key);
if(curpos.x == end.x && curpos.y == end.y) {
PrintPath(&S);
return true;
}
curstep++;
} else {
if(!StackEmpty(S)) {
// 从栈中循环谈栈
Pop(&S, &curpos);
direction = Pass(curpos);
if(direction) {
curpos.direction = direction - 1;
}
// 该块标识为不能通过
MakePrint(curpos, 3);
draw(curpos.x, curpos.y, 4);
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(wait_key);
while(!StackEmpty(S) && curpos.direction == 5) {
Pop(&S, &curpos);
// 该块标识为不能通过
MakePrint(curpos, 3);
}
if(curpos.direction <= 4 && Pass(curpos)) {
curpos.direction++;
Push(&S, curpos);
draw(curpos.x, curpos.y, 3);
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(wait_key);
NextPos(&curpos, curpos.direction);
Push(&S, curpos);
MakePrint(curpos, 2);
draw(curpos.x, curpos.y, 3);
imshow("Maze", mat);
waitKey(wait_key);
if(curpos.x == end.x && curpos.y == end.y) {
PrintPath(&S);
return true;
}
}
}
}
} while(!StackEmpty(S));
return false;
}
int Pass(SElemType pos)
{
// 右
if(pos.y+1 <= n-1 && maze[pos.x][pos.y+1] == 0) {
printf("right\n");
return 1;
}
// 下
// attention
if(pos.x+1 <= n-1 && maze[pos.x+1][pos.y] == 0) {
printf("down\n");
return 2;
}
// 左
if(pos.y-1 >= 1 && maze[pos.x][pos.y-1] == 0) {
printf("left\n");
return 3;
}
// 上
if(pos.x-1 >= 1 && maze[pos.x-1][pos.y] == 0) {
printf("up\n");
return 4;
}
printf("No way!\n");
return 0;
}
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
if(S.top == S.base)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// 1、2、3、4对应的搜索顺序分别为右、下、左、上
void NextPos(SElemType* curpos, int direction)
{
switch(direction) {
case 1: {
curpos->y++;
break;
}
case 2: {
curpos->x++;
break;
}
case 3: {
curpos->y--;
break;
}
case 4: {
curpos->x--;
break;
}
}
}
// 留下标记
void MakePrint(SElemType e, int print)
{
maze[e.x][e.y] = print;
}
运行结果