Section one
SDK & JDK & JRE & IDE
- SDK : Software Development Kit 软件开发工具包
- JDK : Java Development Kit Java开发工具包
- JRE : Java Runtime Environment Java运行时环境
- IDE : Integrated Development Environment 集成开发环境

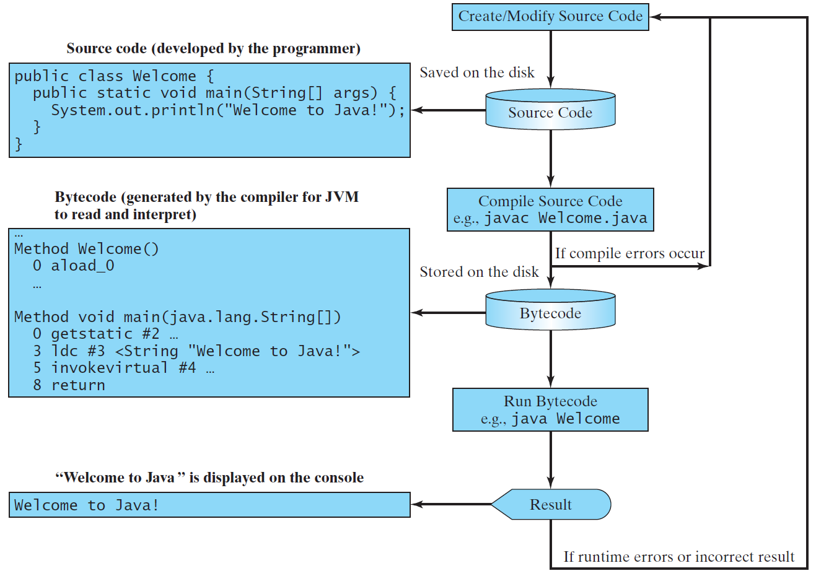
A simple Java Program
源码编写:记事本、文本编辑器、word、notepad++……
源码编译:javac Welcome.java
程序执行:java Welcome.class
// This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Programming Errors
- Syntax Errors 语法错误 初期常见错误
- Runtime Errors 运行时错误 什么时候都可能出现
- Logic Errors 逻辑错误 复杂程序容易出现
Section two
public class ComputerArea {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// define variables
double radius;
double area;
// Assign a radius
radius = 20;
// Compute area
area = radius * radius * 3.14159;
// Display results
System.out.println("The area for the circle of radius " + radius + " is " + area);
}
}
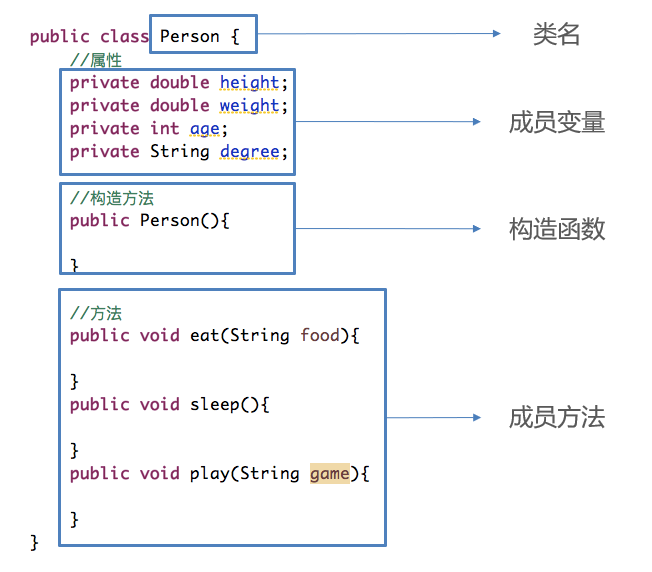
Identifier
- 标识符:常量、变量、类和方法等命名符号
- 规则
- 字母(A~Z、a~z)、特殊符号($、_)和数字(0~9)
- 第1个符号不能为数字
- 不能为关键词、true、false、null
- 区分大小写
- 一般约定
- 表示常量的标识符全部大写,如RED
- 表示类名的标识符用大写字母开始,如MyCar
- 表示公有方法和实例变量的标识符用小写字母开始,后面的描述性词以大写开始,如getCurrentValue
- 表示私有或局部变量的标识符全部用小写字母,如next_value
| Name | Range | Storage size |
|---|---|---|
| byte | –2**7** to 2**7** – 1 (-128 to 127) | 1 byte |
| short | –2**15** to 2**15** – 1 (-32768 to 32767) | 2 bytes |
| int | –2**31** to 2**31** – 1 (-2147483648 to 2147483647) | 4 bytes |
| long | –2**63** to 2**63** – 1 (-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) | 8 bytes |
| float(**单精度**) | Negative: -3.4028235E+38 to -1.4E-45 Positive: 1.4E-45 to 3.4028235E+38 | 4 bytes |
| double(**双精度**) | Negative : -1.7976931348623157E+308 to -4.9E-324 Positive : 4.9E-324 to 1.7976931348623157E+308 | 8 bytes |
int x = 1;
long x = 8864L; (or 8864l)
float d = 1.4F; (or 1.4f)
double d = 1.4; (or 1.4D 1.4d)
char a = 'A';// long:8字节8864在long表示的范围内
long x = 8864;
// JVM中整型默认以int存储
// 自动类型转换(升级)long x = 100000000000;
// 错,10e11超过了int的最大范围
// JVM int: 10e11long x = 100000000000L;
// 正确,10e11在long的取值范围内float x = 0.14;
// float:4字节
// Doublefloat,8字节向4字节,精度可能丢失
// double: 0.14
// JVM默认把0.14看成是Double型的float x = 0.14F;
// float:4字节
// 正确
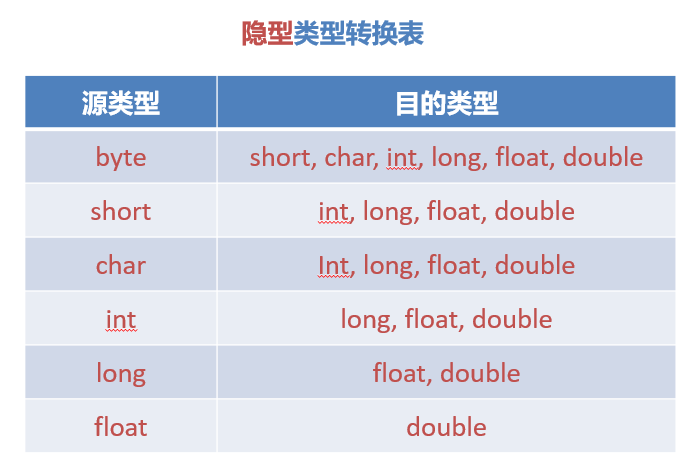
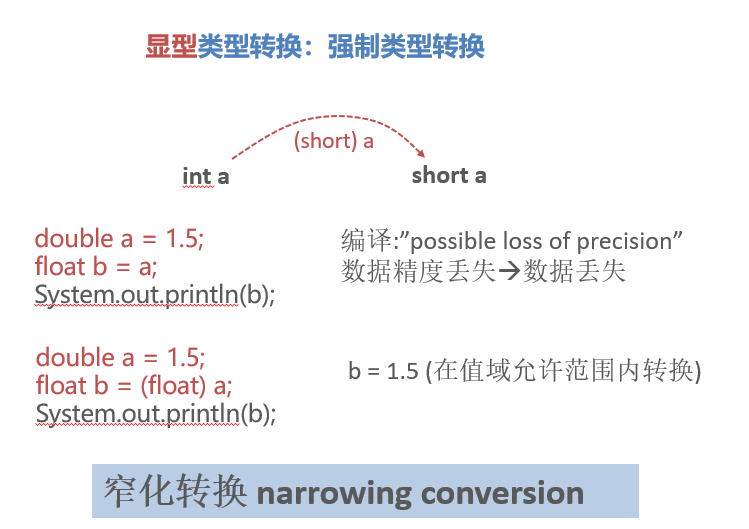
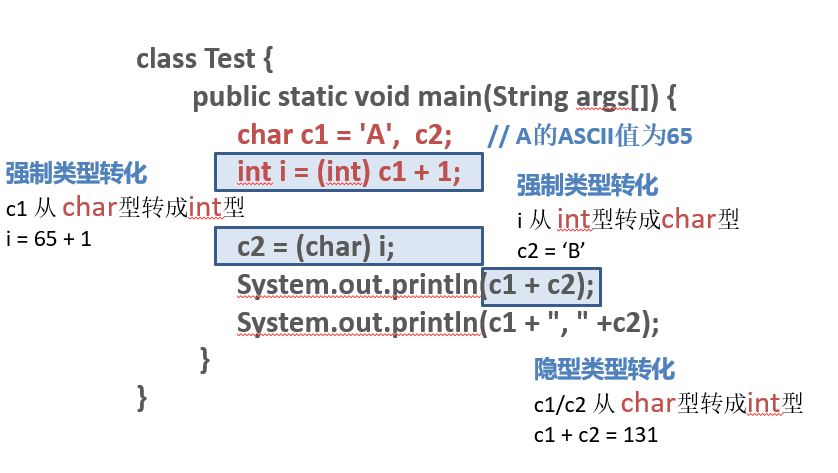
Type Casting
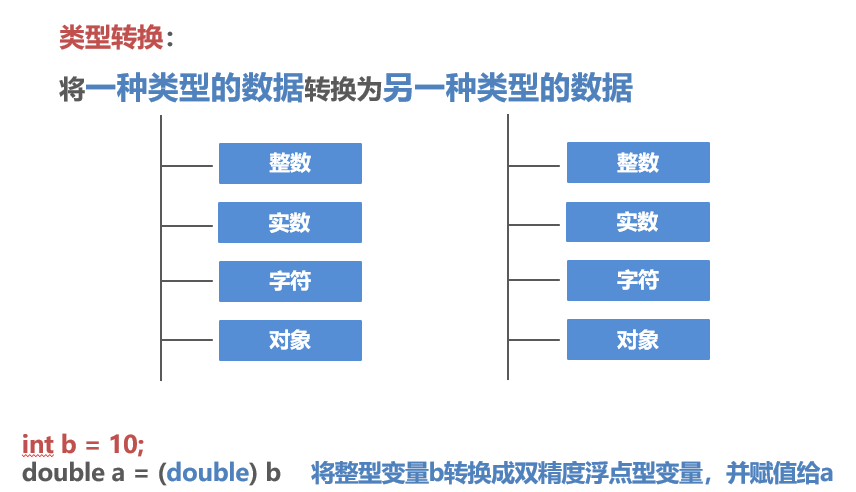
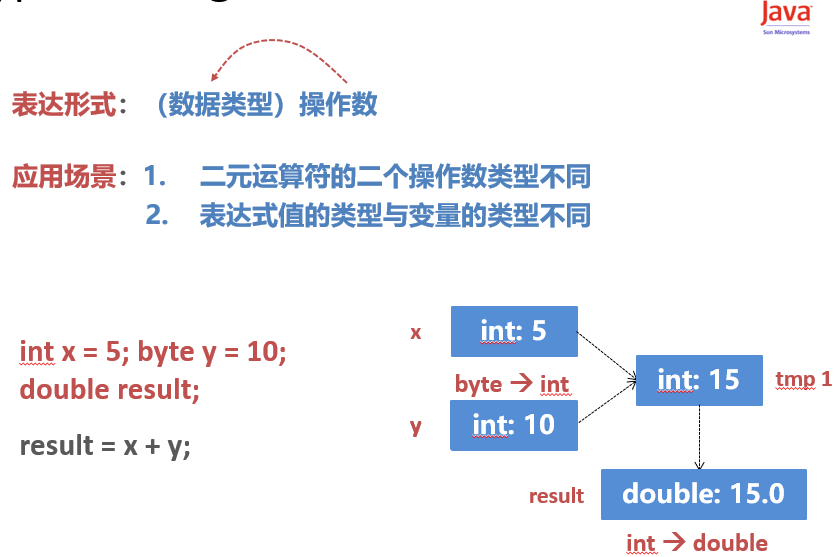
转换方法
- 1. 隐型类型转换:自动类型转换(系统完成)
- 2. 显型类型转换:强制类型转换


Section three
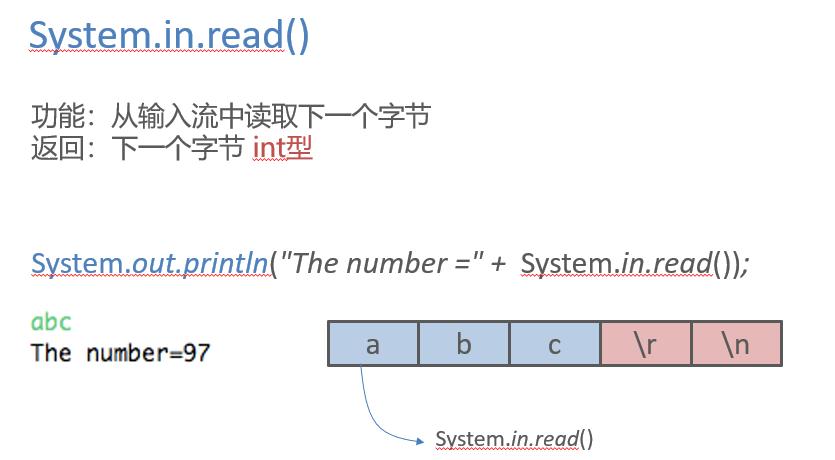
System.in.read()
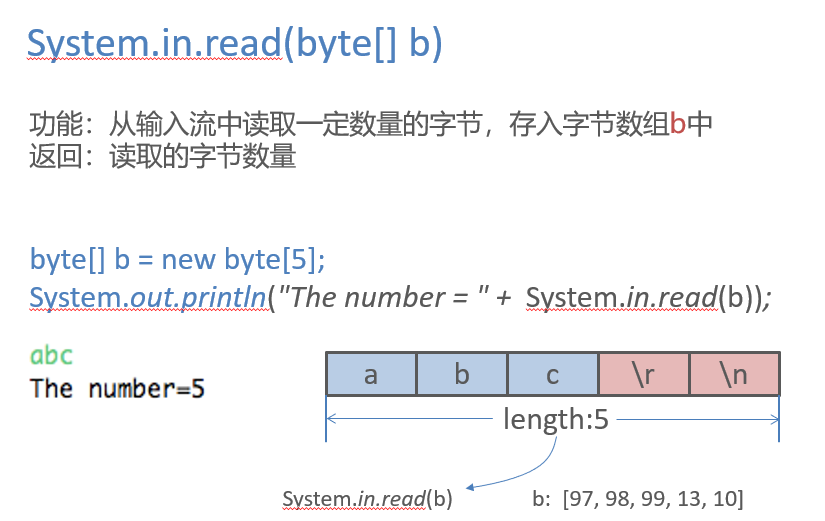
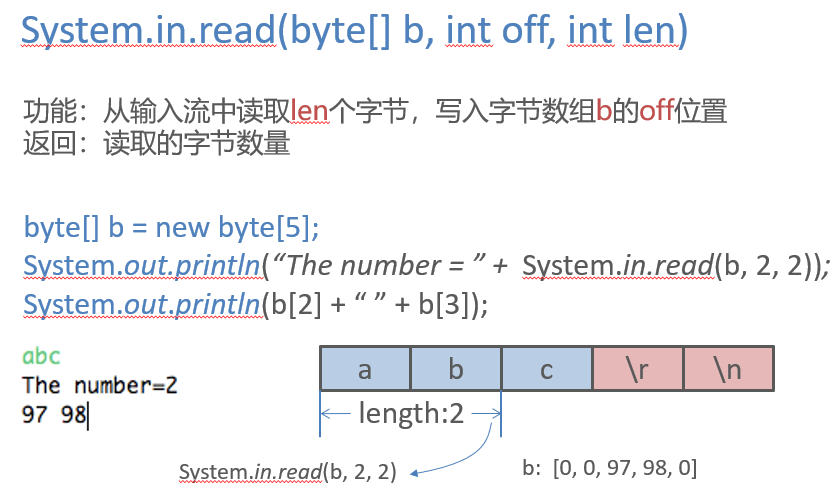



Scanner
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please input string: ");
System.out.println(s.nextLine());
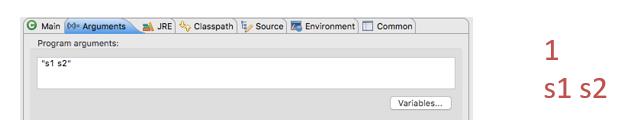
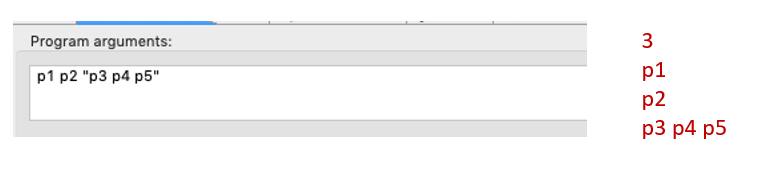
public static void main(String[] args) {
int len = args.length;
System.out.println(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
// 依次打印主程序的输入参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++)
sum = sum + Integer.parseInt(args[i]);
System.out.println(sum);
}
// 计算输入参数之和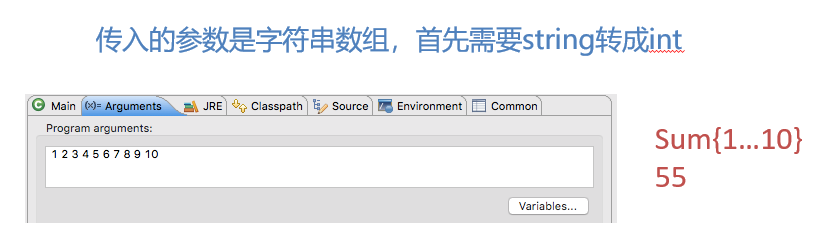
Section four



方式一: 声明和创建数组后对数组初始化
class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = new int[5];
System.out.println(“\t输出一维数组a: ”);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
a[i] = i+1;
System.out.println(“a[”+i+“]=”+a[i]);
}
}
}
// a[0]=1
// a[1]=2
// a[2]=3
// a[3]=4
// a[4]=5
方式二: 声明数组的同时对数组初始化
class Welcome {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(“\t输出一维数组a: ”);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(“\ta[”+i+“]=”+a[i]);
}
}
}Initializing arrays with input values
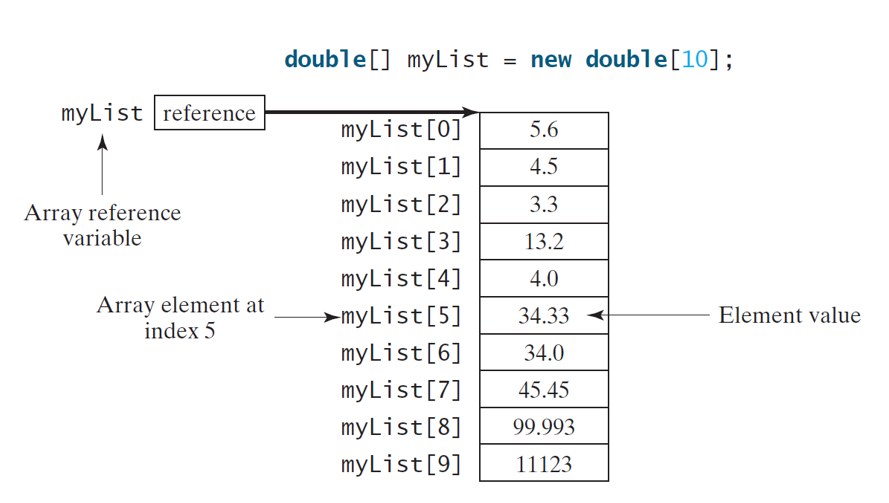
double[] myList = new double[10];
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter " + myList.length + " values: ");
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
myList[i] = input.nextDouble();
Initializing arrays with random values
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
myList[i] = Math.random()*100;
// 以[0,100)之间的随机数初始化Printing arrays
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
System.out.println(myList[i]);Summing all elements
total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
total += myList[i];Finding the largest element
double max = myList[0];
for (int i = 1; i < myList.length; i++) {
if (myList[i] > max)
max = myList[i];
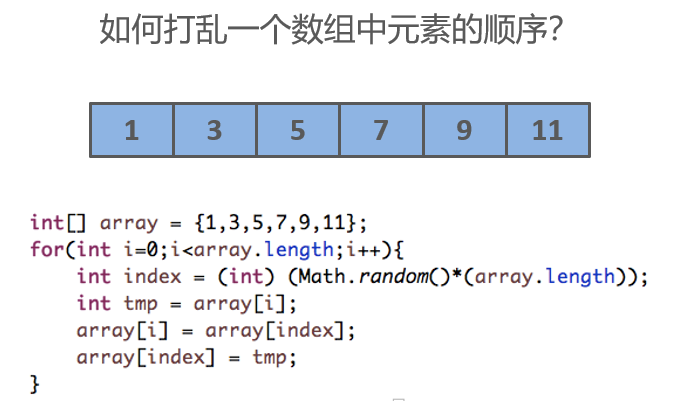
}Random shuffling
Shifting elements

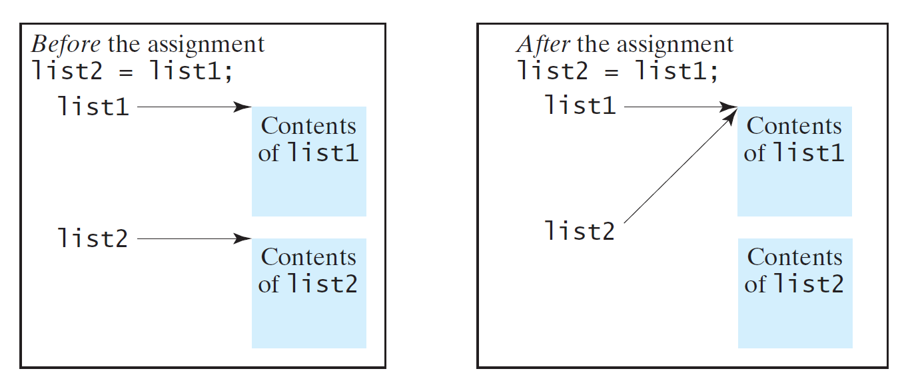
Array assignment
方法一:数组的整体赋值
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int b[]; int[] c = {1, 3, 5, 7};
b = a; c = a;
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++)
System.out.print(a[j] + “ “);
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++)
System.out.print(b[j] + “ “) ;
System.out.println();
for (int j = 0; j < c.length; j++)
System.out.print(c[j] + “ “);
}
C:\>java Test
2 4 6 8
2 4 6 8
2 4 6 8
C:\>
方法二:数组遍历赋值
int[] sourceArray = {2, 3, 1, 5, 10};
int[] targetArray = new int[sourceArray.length];
for (int i = 0; i < sourceArrays.length; i++)
targetArray[i] = sourceArray[i];
方法三:java.lang.System类的方法 arraycopy
arraycopy(Object src, int srcIndex, Object dest, int destIndex, int length)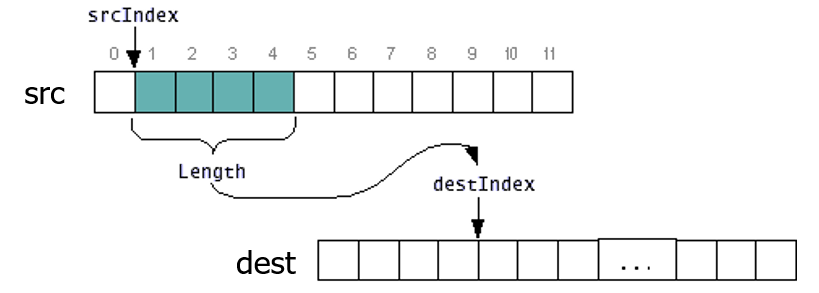
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int b[];
int[] c = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
b = a;
System.arraycopy(a, 1, c, 0, 3);
//打印a,b,c
}
// 数组a: 2 4 6 8
// 数组b: 2 4 6 8
// 数组c: 4 6 8 7 9
Declaring and creating
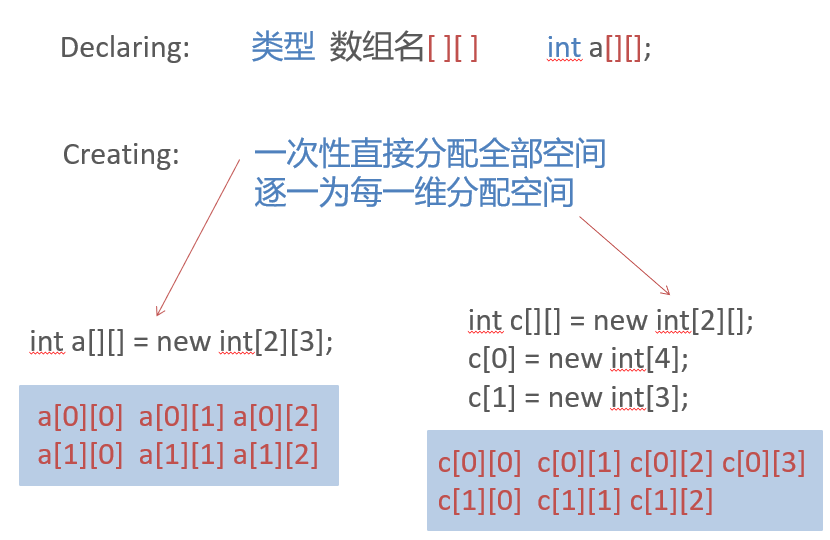
Initializer

Example


Simple method of String

Getting string length
String message = "Welcome to Java";
System.out.println(message.length());
// message.length() = 15*Getting Characters from a String *
String message = "Welcome to Java";
System.out.println("The first character in message is " + message.charAt(0));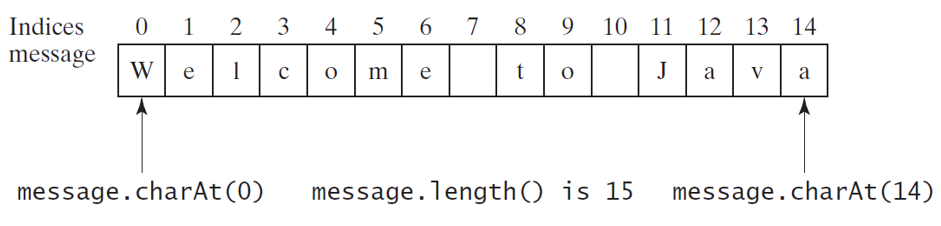
Converting Strings
“Welcome”.toLowerCase() 返回小写字符串 “welcome”
“Welcome”.toUpperCase() 返回大写字符串 “WELCOME”
“ Welcome ”.trim() 删除前后空格 “Welcome”*String Concatenation *
String s3 = s1.concat(s2); or String s3 = s1 + s2;
// Three strings are concatenated
String message = "Welcome " + "to " + "Java";
String message = “Welcome”.concat(“ to”).concat(“ Java”);
// String Chapter is concatenated with number 2
String s = "Chapter" + 2; // Chapter2
// String Supplement is concatenated with character B
String s1 = "Supplement" + 'B'; // SupplementB*Reading a String from the Console *
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter three words separated by spaces: ");
String s1 = input.nextLine();
String s2 = input.nextLine();
String s3 = input.nextLine();
System.out.println("s1 is " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 is " + s2);
System.out.println("s3 is " + s3);
// This is Arsenal 回车
// This is Livepool 回车
// This is MU 回车
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter three words separated by spaces: ");
String s1 = input.next();
String s2 = input.next();
String s3 = input.next();
System.out.println("s1 is " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 is " + s2);
System.out.println("s3 is " + s3);
// This is 回车
// Arsenal Fan 回车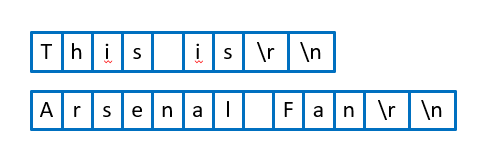
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter three words separated by spaces: ");
String s1 = input.nextLine();
String s2 = input.next();
String s3 = input.next();
System.out.println("s1 is " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 is " + s2);
System.out.println("s3 is " + s3);
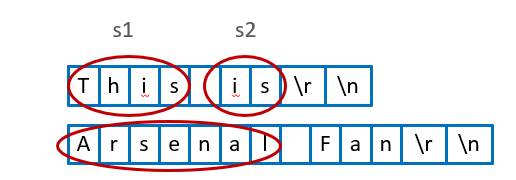
// This is 回车
// Arsenal Fan 回车
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter three words separated by spaces: ");
String s1 = input.next();
String s2 = input.next();
String s3 = input.nextLine();
System.out.println("s1 is " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 is " + s2);
System.out.println("s3 is " + s3);
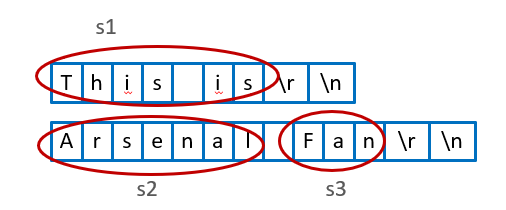
// This is Arsenal Fan 回车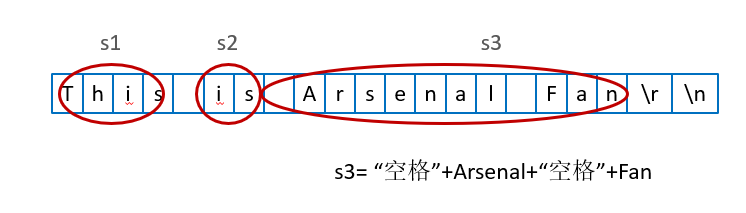
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("输入第一个字符串: ");
String s1 = input.next();
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.print("输入第二个字符串: ");
String s2 = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(s2);
// 我们在上课 回车

Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("输入第一个字符串: ");
String s1 = input.next();
System.out.println(s1);
input.nextLine();
System.out.print("输入第二个字符串: ");
String s2 = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(s2);
// 我们在上课 回车
// 我们在上JAVA课 回车
Comparing Strings

Obtaining Substrings

Finding a Character or a Substring in a String







Obtaining Substrings

int k = s.indexOf(' ');
String firstName = s.substring(0, k);
String lastName = s.substring(k + 1);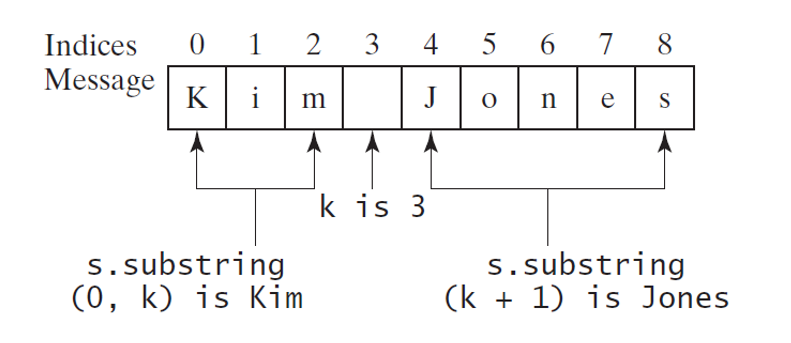
int/double… String
// String to int/double
int intValue = Integer.parseInt(intString);
double doubleValue = Double.parseDouble(doubleString);
// int/double to String
int number = 2;
String s = number; //Error
String s = number + "";
Section five
Interface
Inheritance(继承)
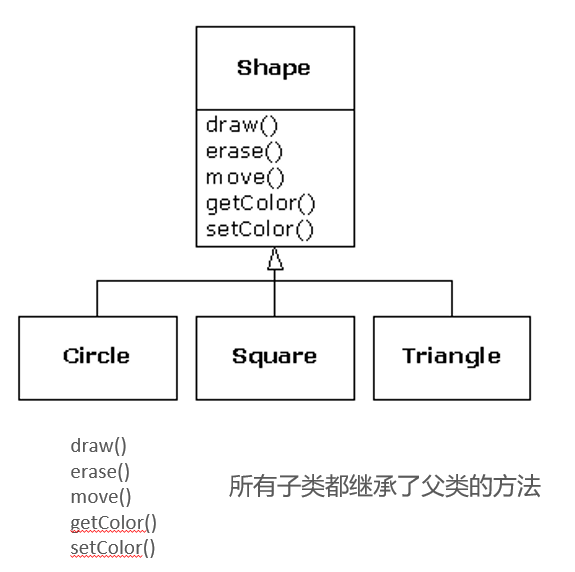
Polymorphism(多态)
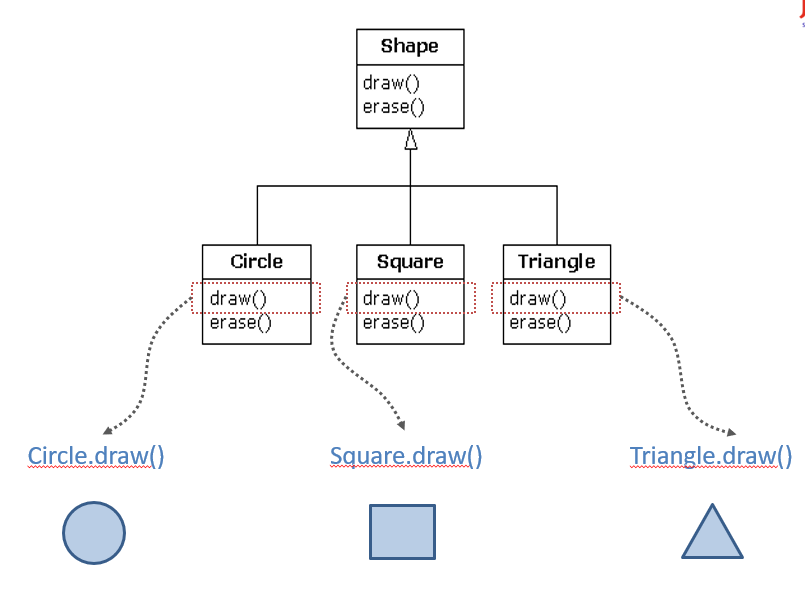
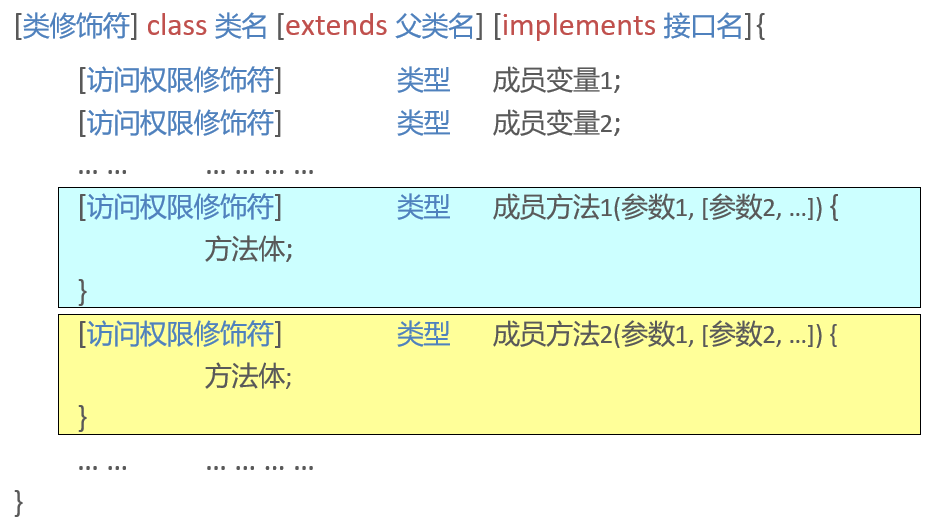
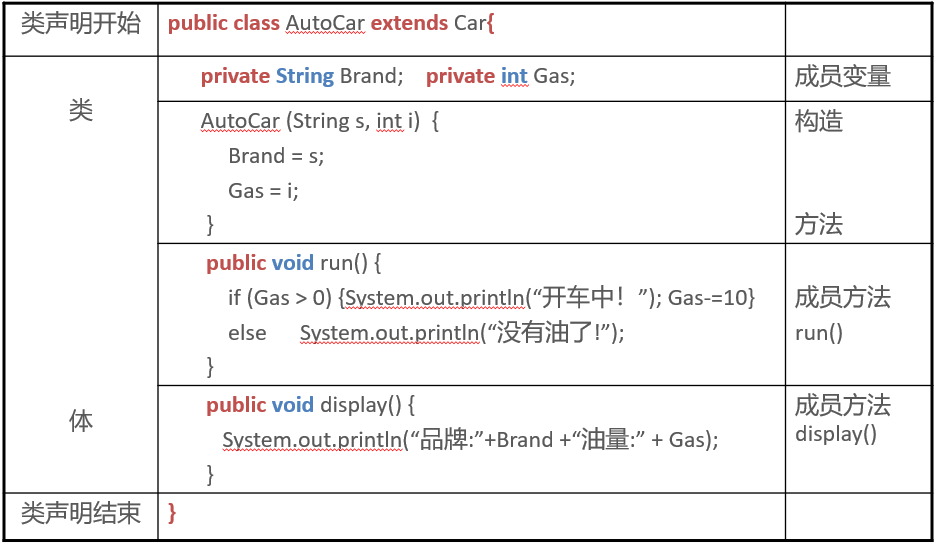
How to define a Class
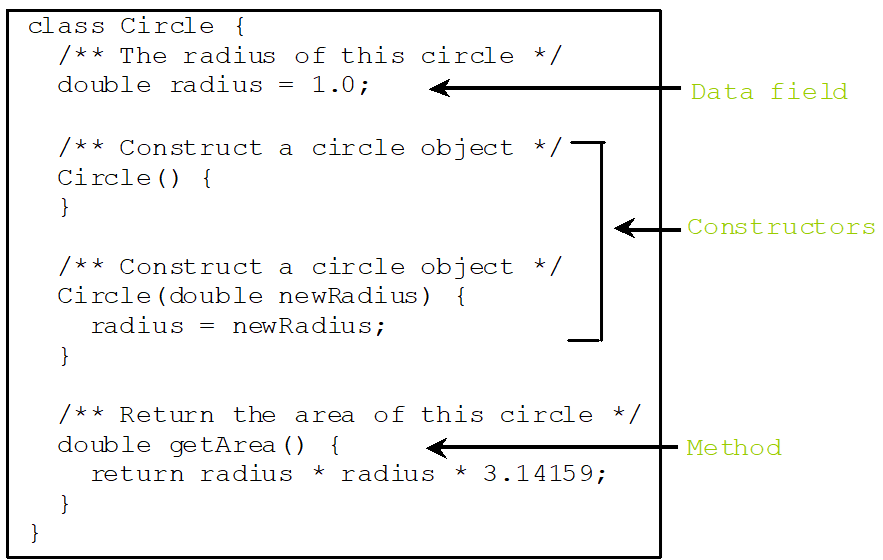
class Test {
public static void main(String args[]){
AutoCar mycar = new AutoCar(“Audi”, 10);
mycar.display();
mycar.run();
mycar.run();
}
}D:\>java Test
品牌: Audi 油量: 10
开车中!
没有油了!Class modifier

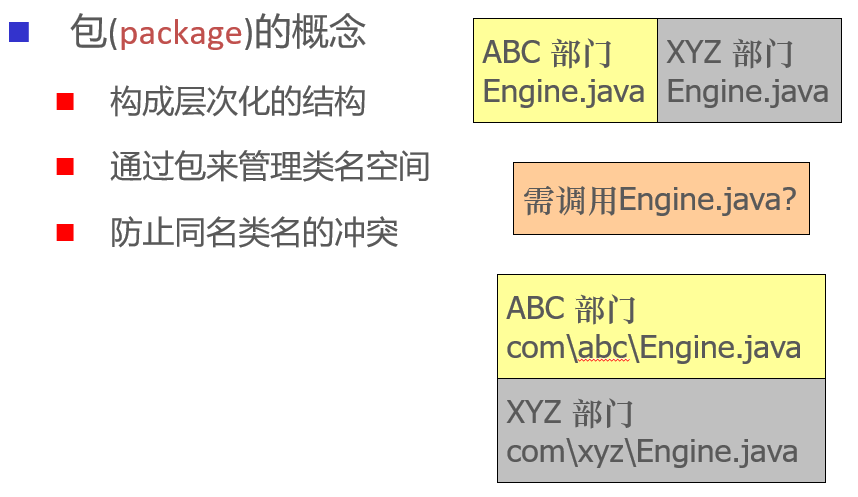
Package
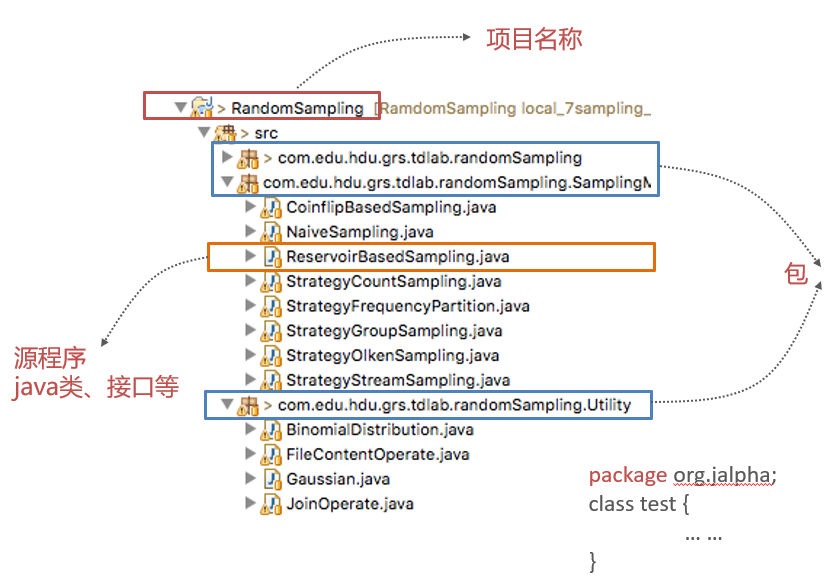
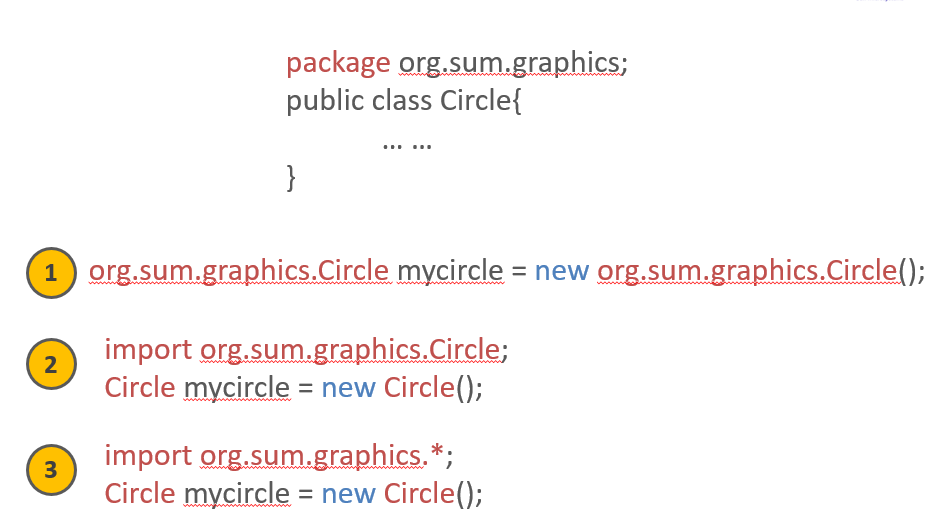
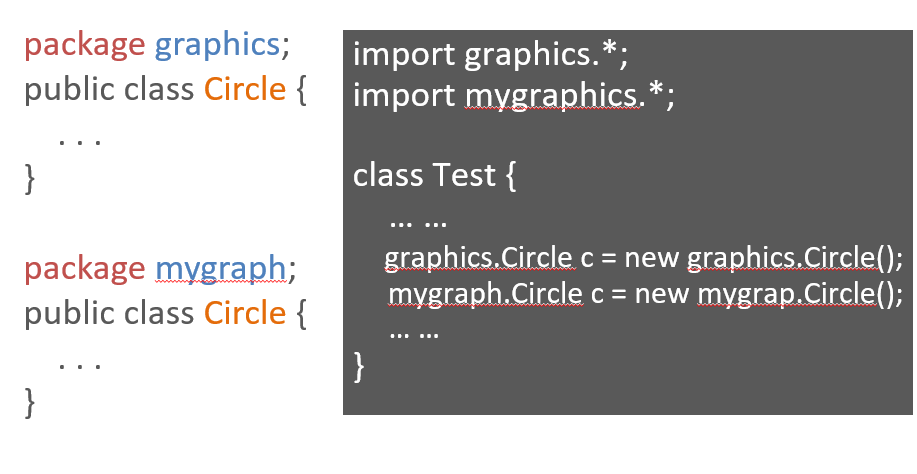

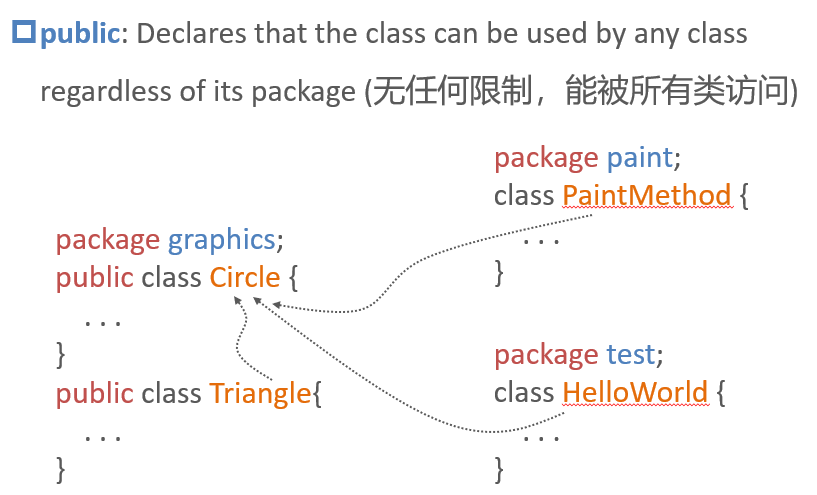
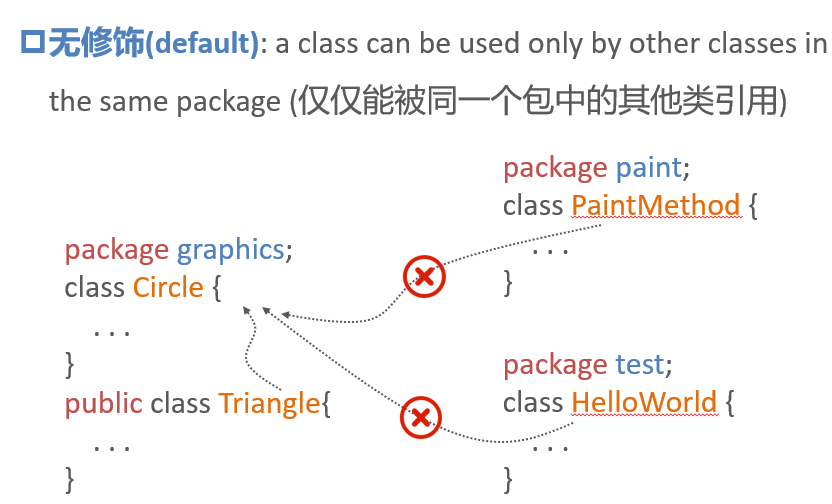
Class modifier

Class members
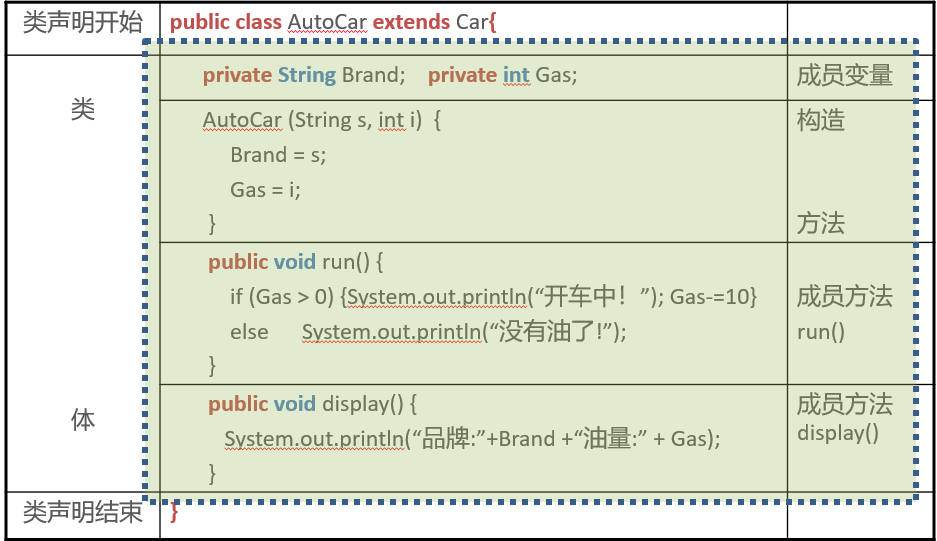
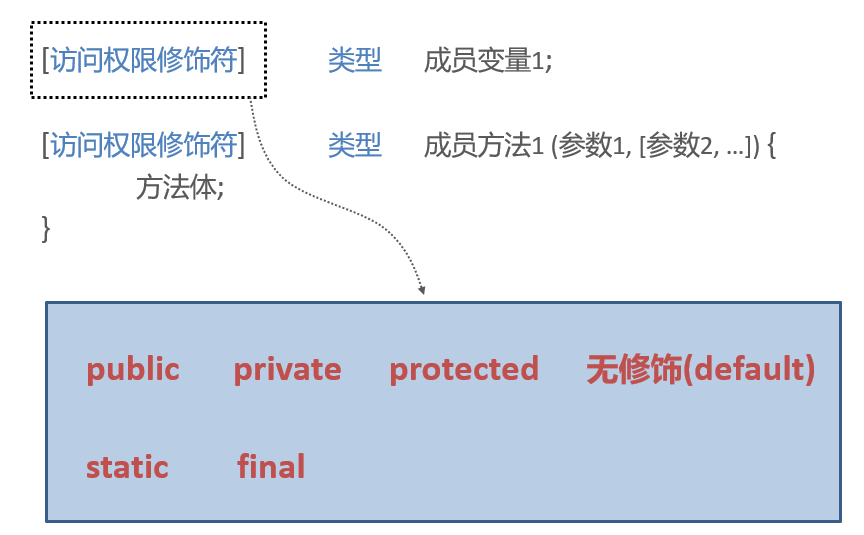
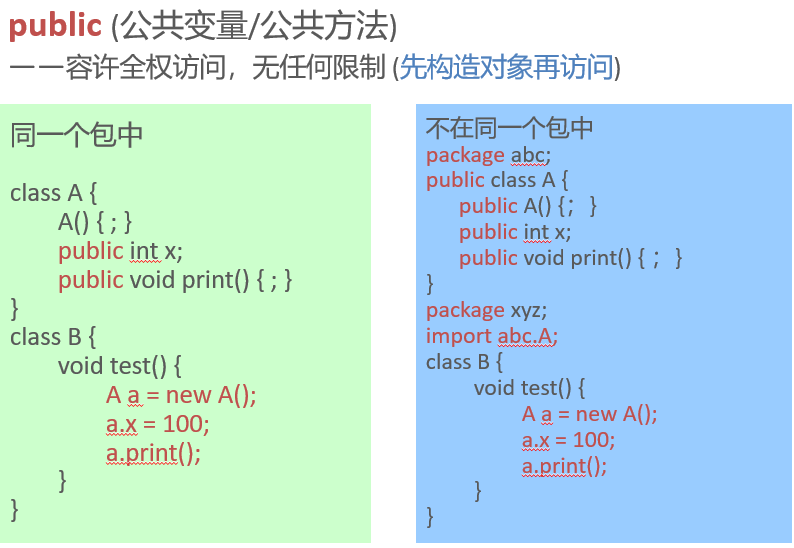
Public members
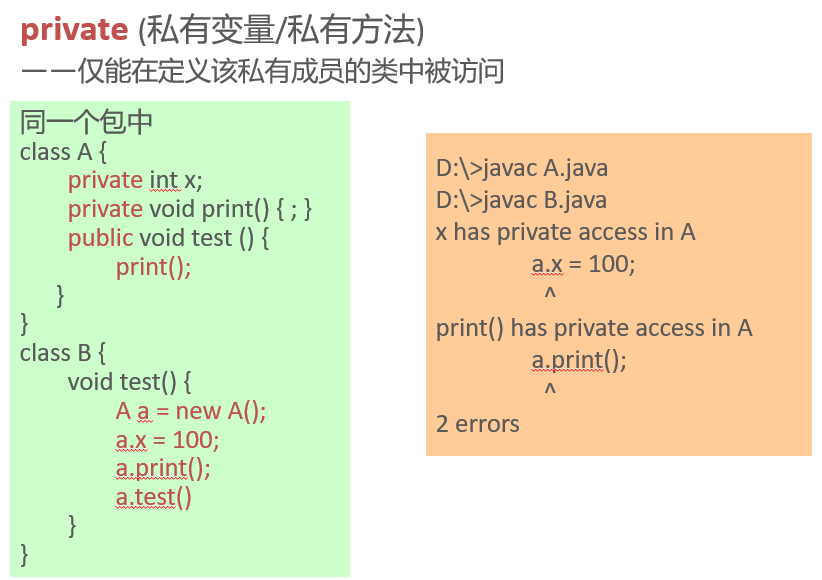
Private members
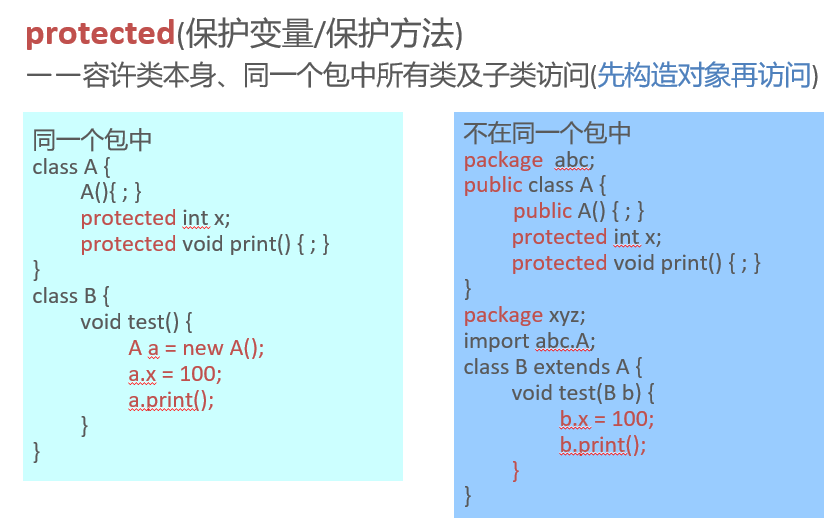
Protected members

Conclusion
Statics members

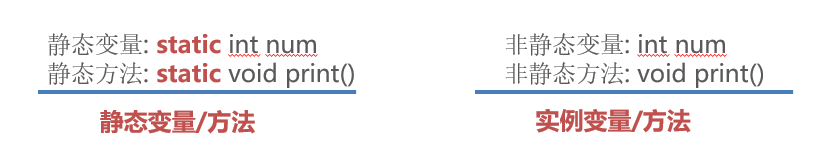
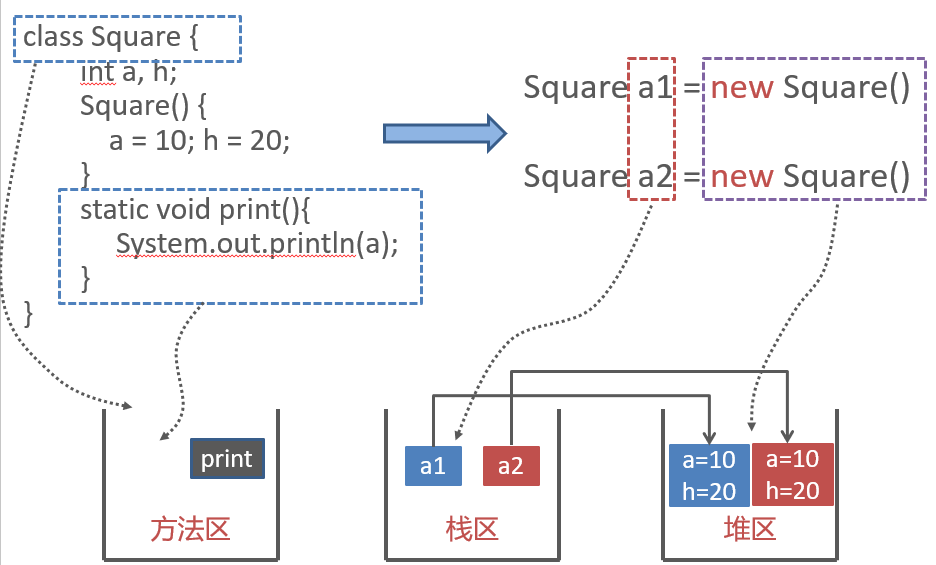
Object creating
class Test {
Test() { ; }
public void print(int x) {
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 3;
Test t = new Test();
t.print(x);
}
}class Test {
Test() { ; }
public static void print(int x) {
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 3;
print(x);
}
}class Test {
public void print(int x) {
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 3;
print(x);
}
}
D:\>javac Test.java
Test.java:9: non-static method print(int)
cannot be referenced from a static context
print(x);
^
1 error
Final members
final(常量/不可重写的方法)
——定义常量以及确保一个方法不可被子类重写
同一个包中
class A {
A(){ ; }
final int PI = 3.14159;
final void print() {
System.out.println(“A print”);
}
}
class B extends A{
PI = 3.1415926; // 常量不可改变取值
// 不可被子类重写
void print(){
System.out.println(“B print”);
}
}
final 变量:变量值不可修改
final 方法:不能被重写(overriding),即不能被子类重新定义
class A {
final int x;
final void print() {
System.out.println(“1”);
}
}
class B extends A {
void print() {
System.out.println(“2”);
}
}
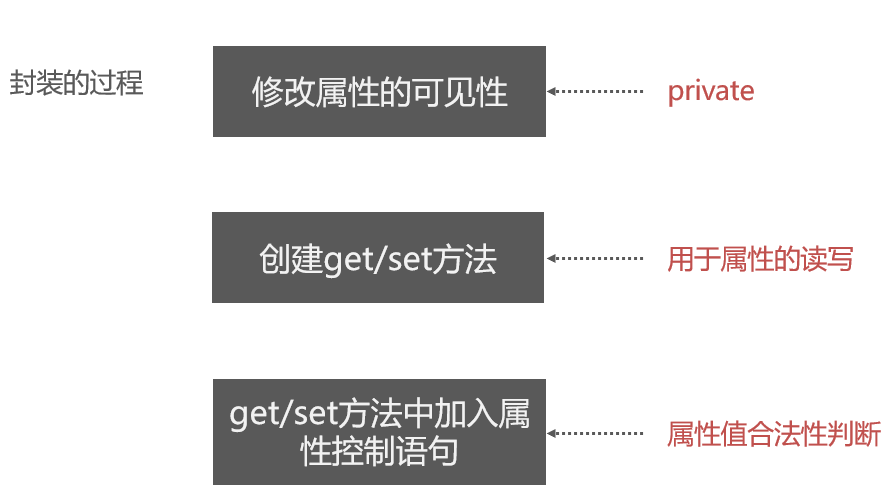
Encapsulation





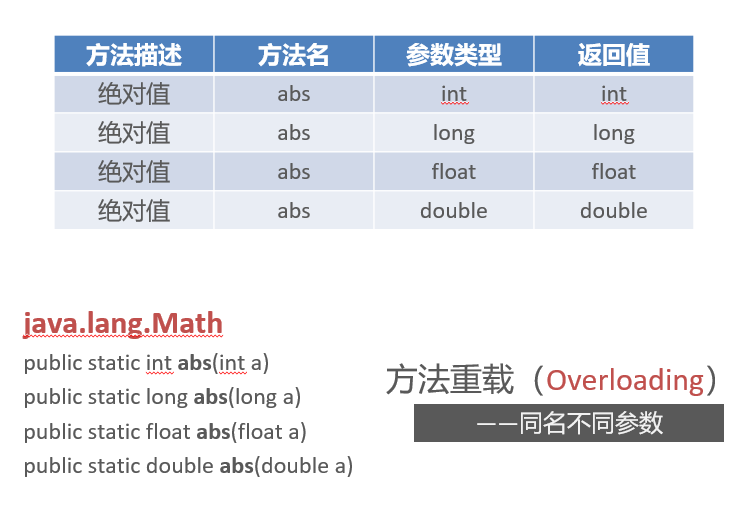
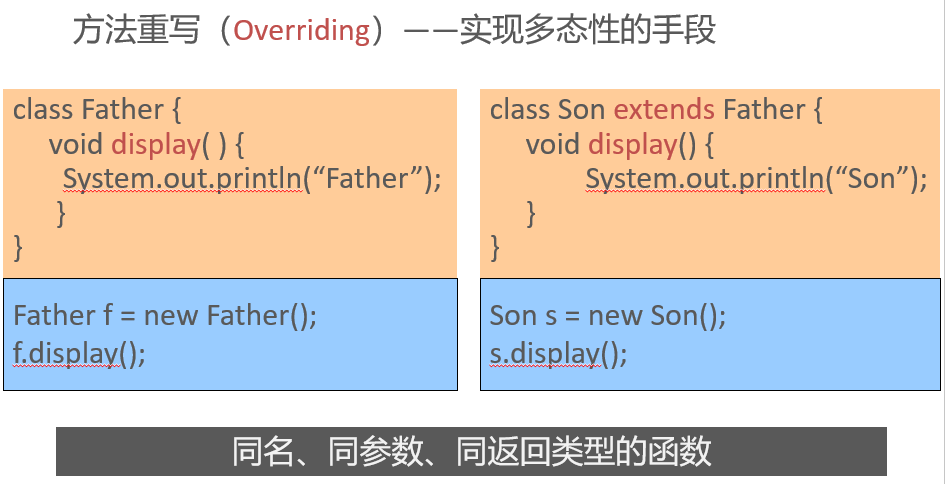
Overloading & Overriding
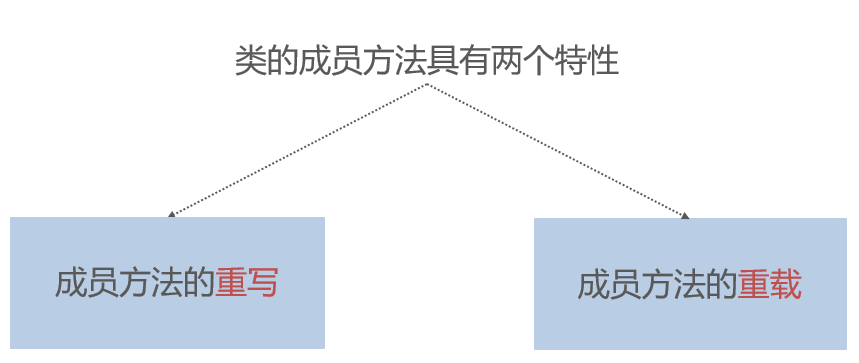

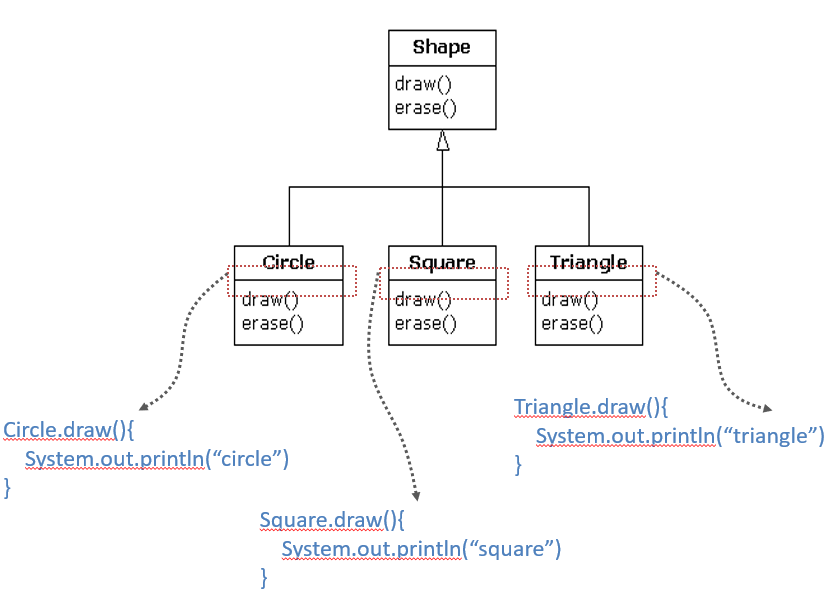
Overriding vs. Overloading
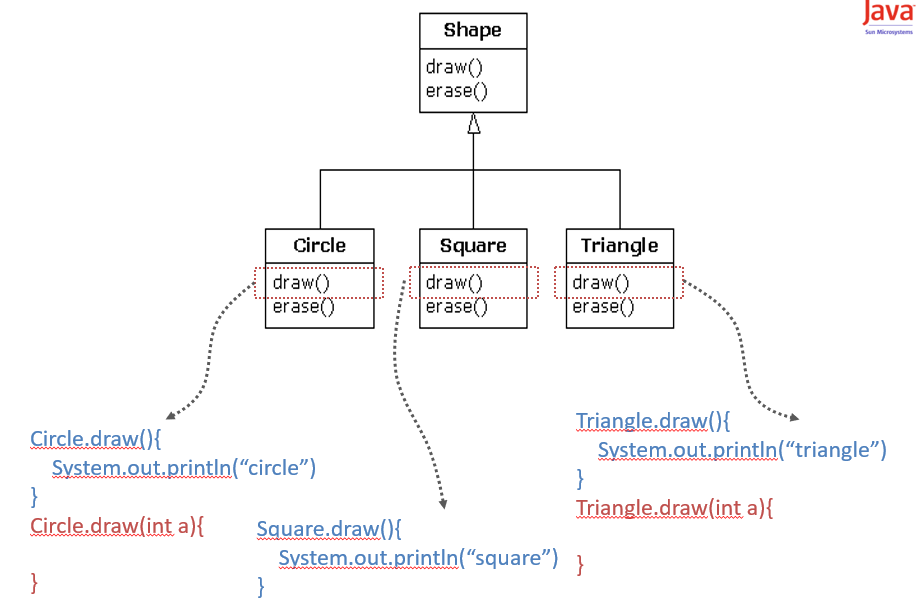
Section six
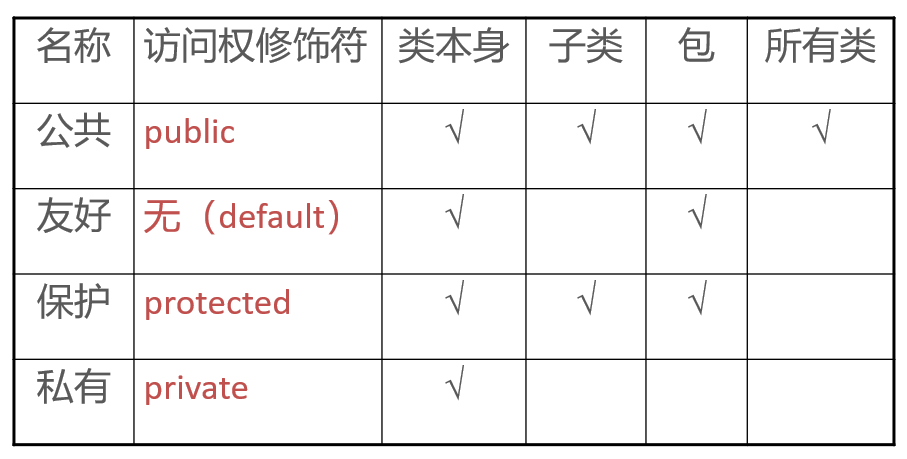
| 名称 | 访问权修饰符 | 类本身 | 子类 | 包 | 所有类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 公共 | public | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| 友好 | 无(default) | √ | √ | ||
| 保护 | protected | √ | √ | √ | |
| 私有 | private | √ |
Object usage


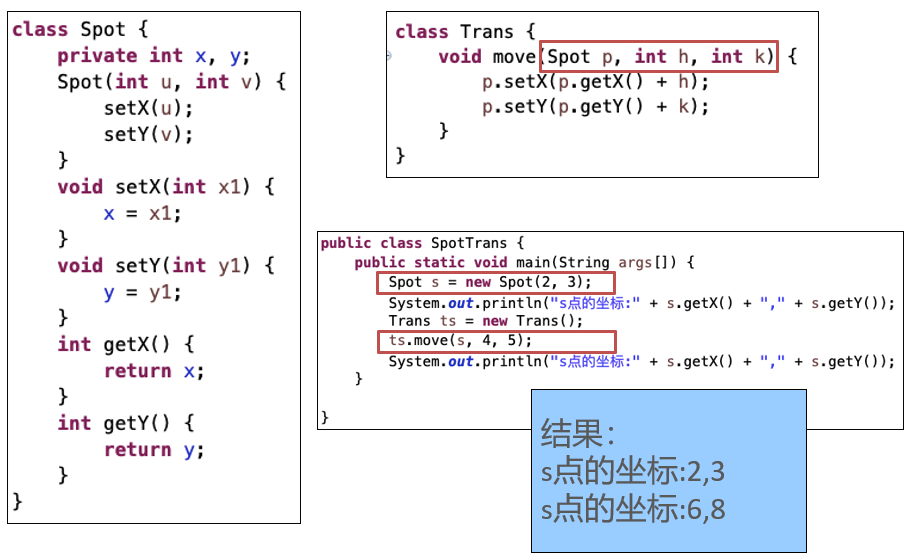
对象作为方法的参数
class Spot {
private int x, y;
Spot (int u, int v) {
setX(u); setY(v);
}
void setX(int x1) { x=x1; }
void setY(int y1) { y=y1; }
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
static void move(Spot p, int h, int k){
p.setX(p.getX() + h);
p.setY(p.getY() + k);
}
}class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Spot s = new Spot(2, 3);
System.out.println(“s点的坐标:” + s.getX()+“,”+s.getY());
Spot.move(s, 4, 5);
System.out.println(“s点的坐标:” + s.getX()+“,”+s.getY());
}
}
D:\java Test
s点的坐标:2,3
s点的坐标:6,8class Spot {
private int x, y;
Spot (int u, int v) {
setX(u); setY(v);
}
void setX(int x1) { x=x1; }
void setY(int y1) { y=y1; }
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
void move(int h, int k){
x = x + h;
y = y + k;
}
}class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Spot s = new Spot(2, 3);
System.out.println(“s点的坐标:” + s.getX()+“,”+s.getY());
s.move(4, 5);
System.out.println(“s点的坐标:” + s.getX()+“,”+s.getY());
}
}D:\java Test
s点的坐标:2,3
s点的坐标:6,8对象作为方法的返回值

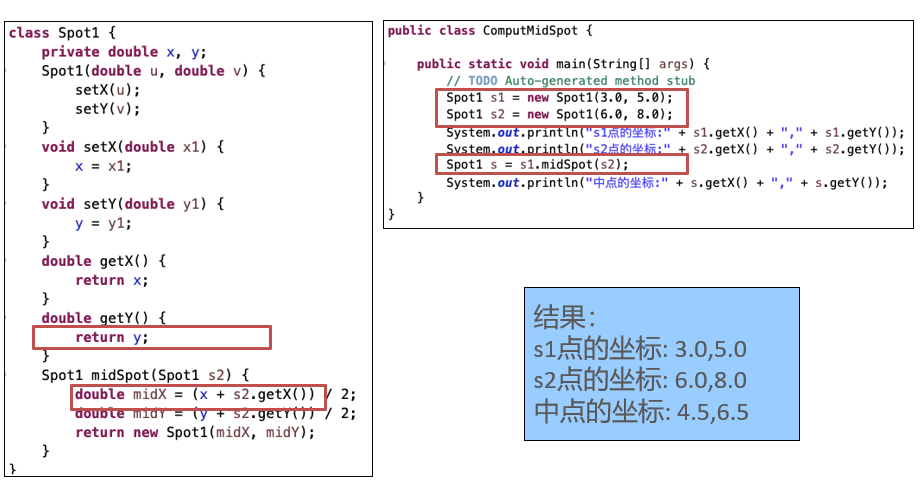
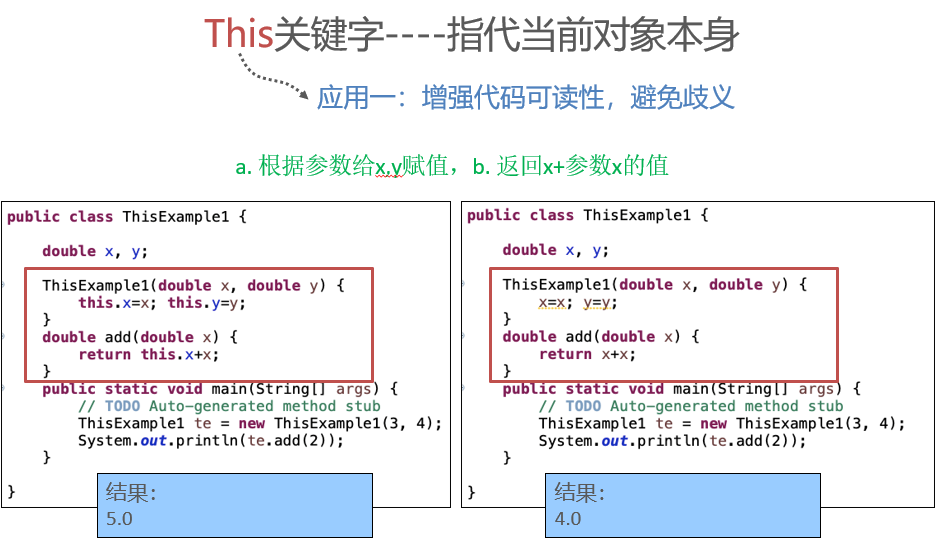
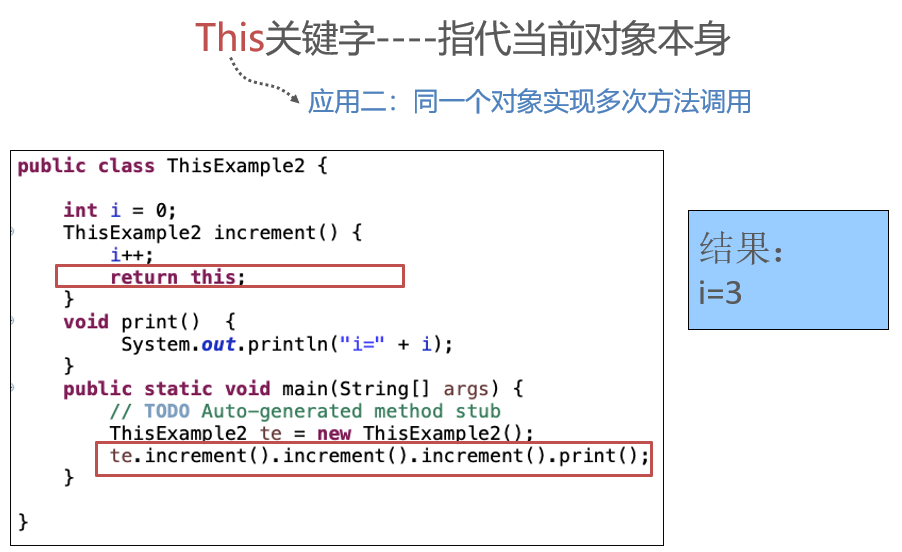

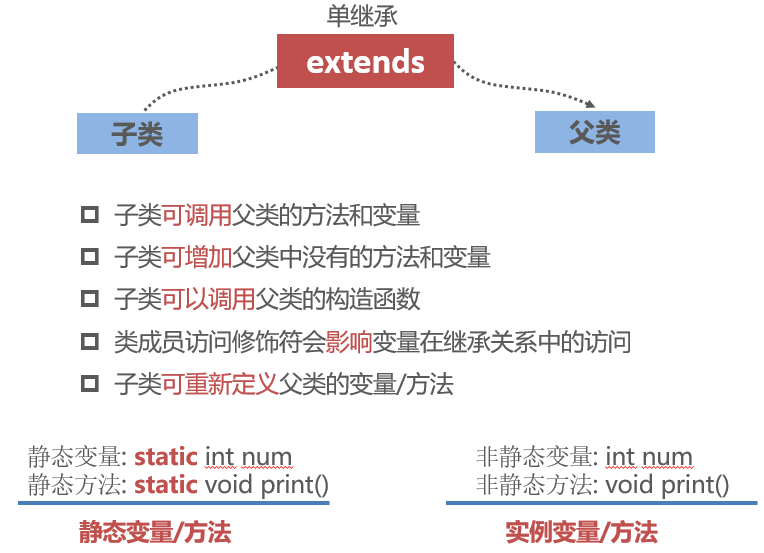
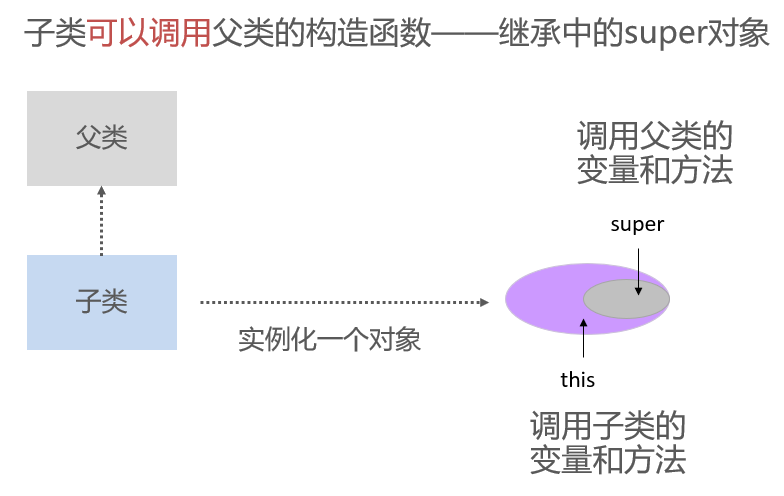
Inheritance of Class

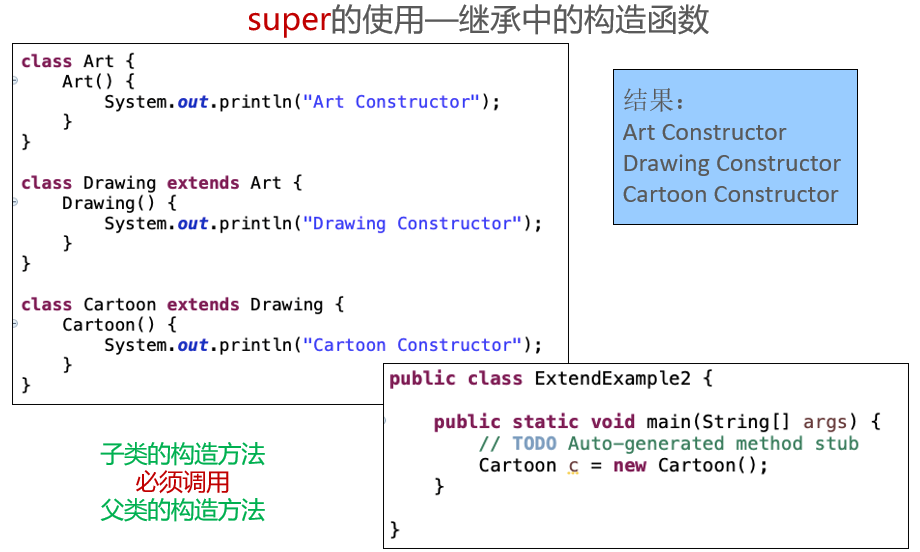
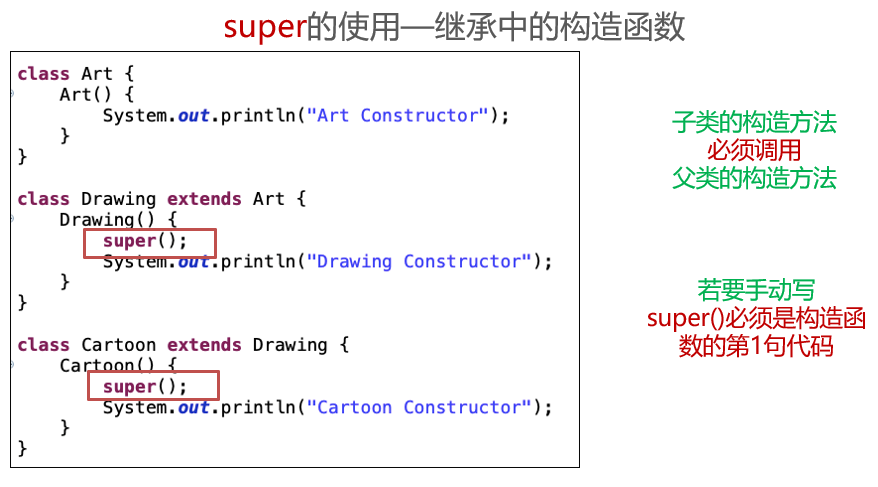
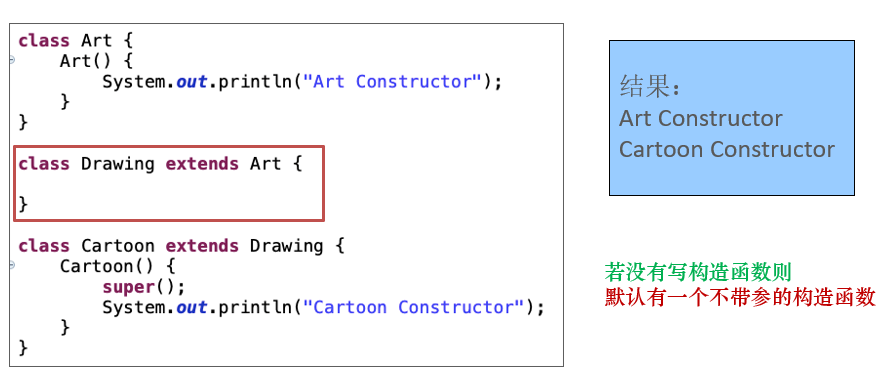
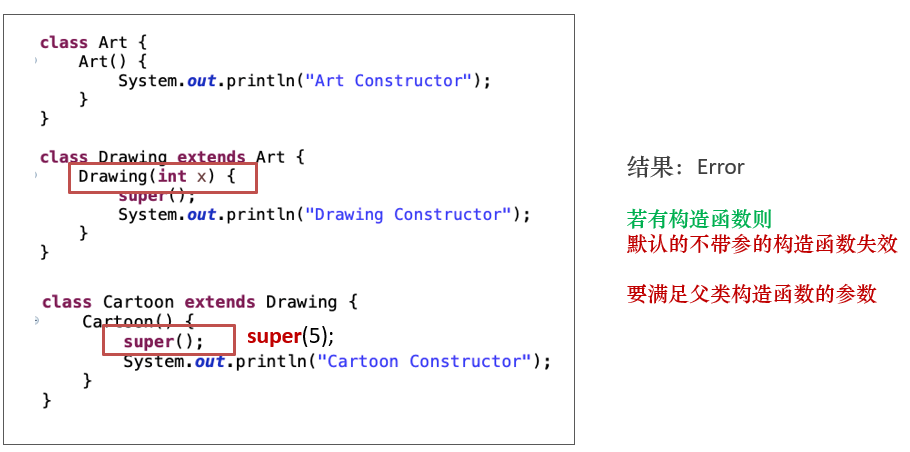


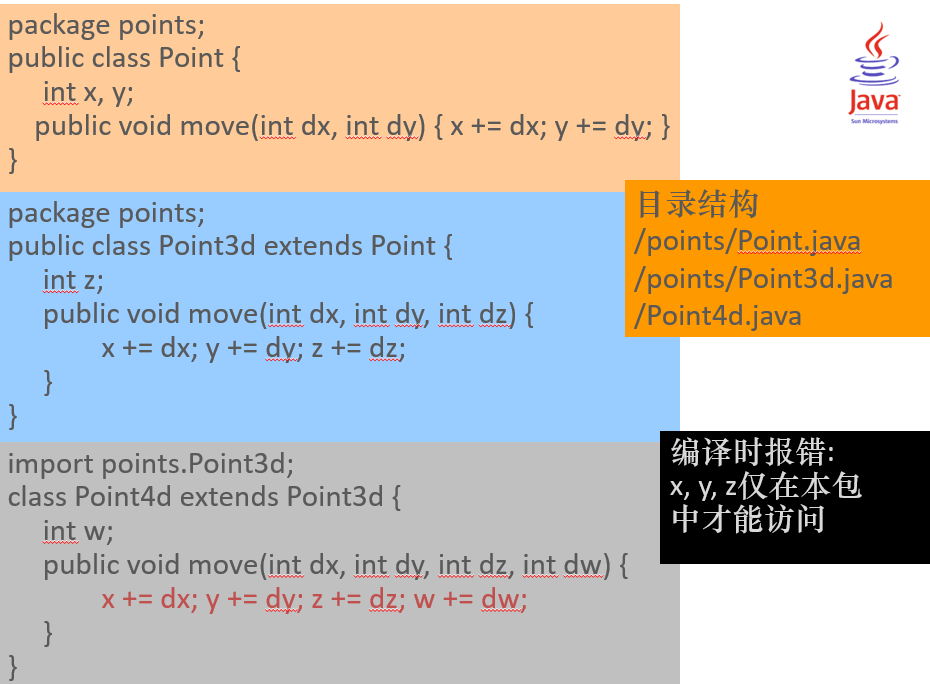



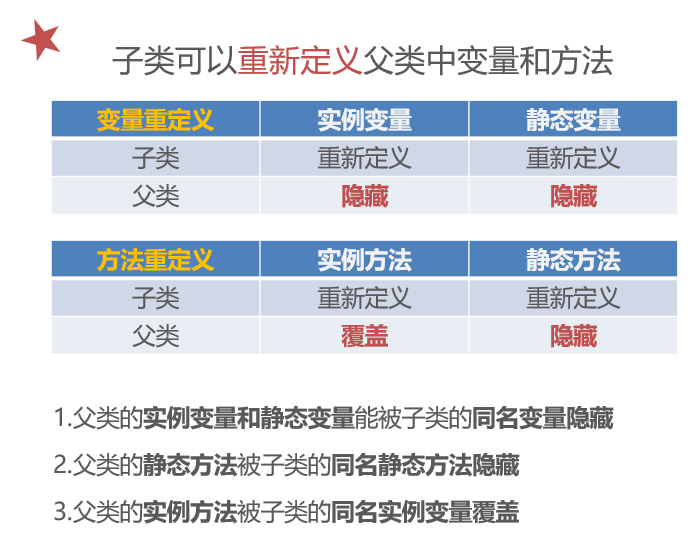
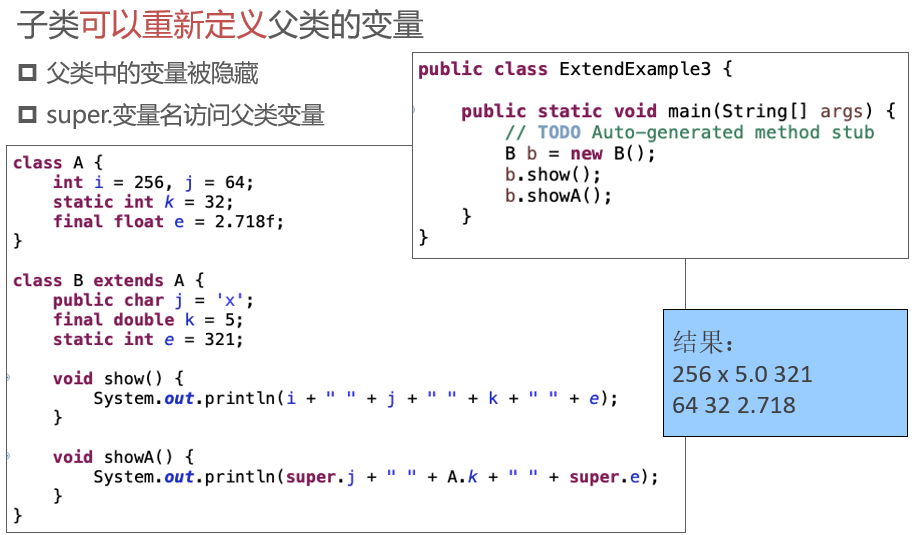
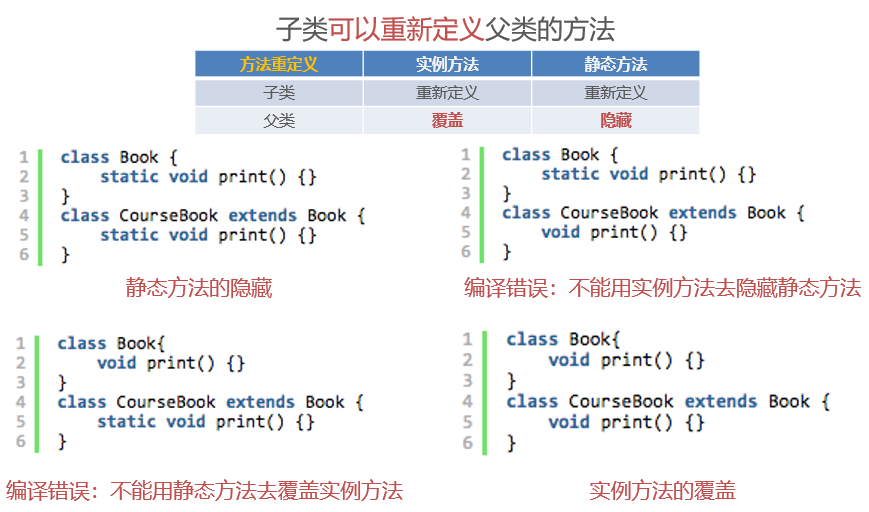
class Father {
public void set() {}
static void get() {}
}class Son extends Father {
public void set() {}
static void get() {}
}
// RIGHT!class Son extends Father {
public void get() {}
static void set() {}
}
// WRONG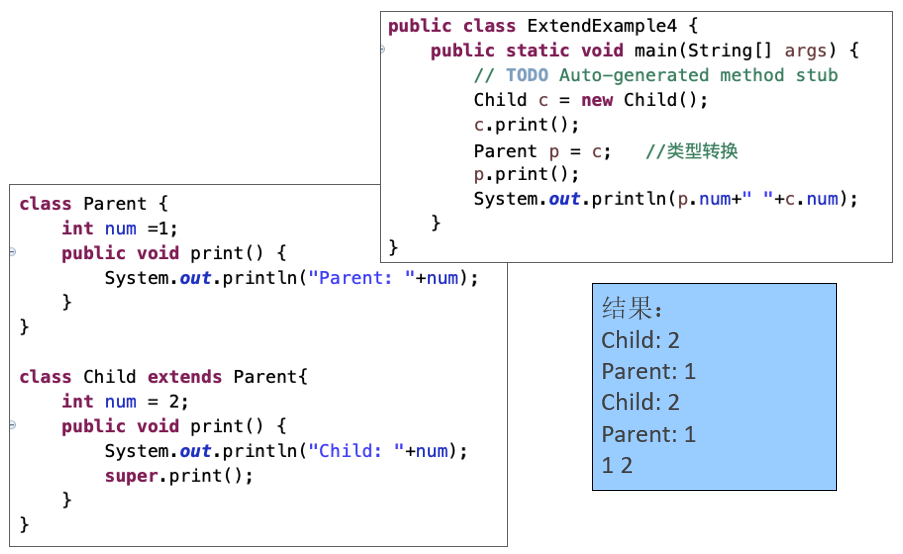
子类重写了print()方法,那么父类类型的引用child在调用该方法时将会调用子类中重写的print()。
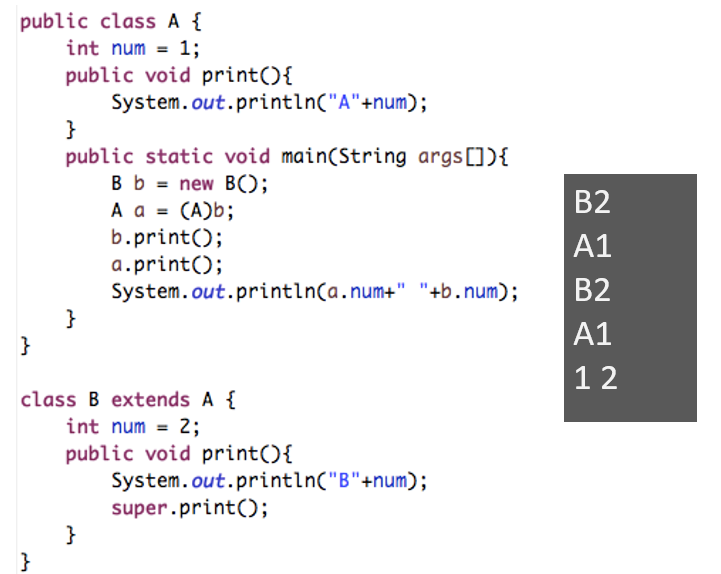
子类重写了print()方法,那么父类类型的引用child在调用该方法时将会调用子类中重写的print()。同上
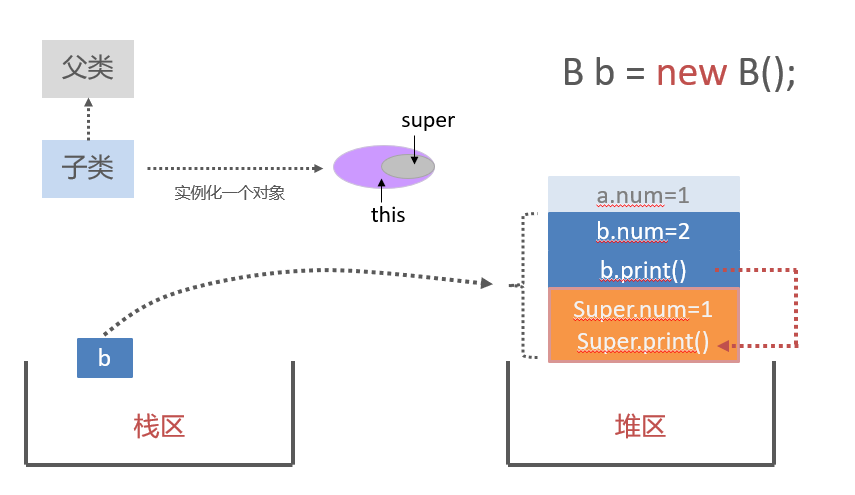
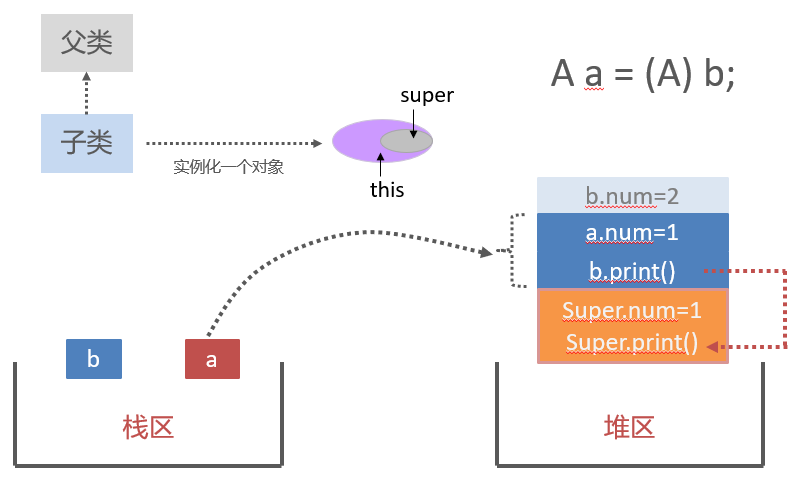
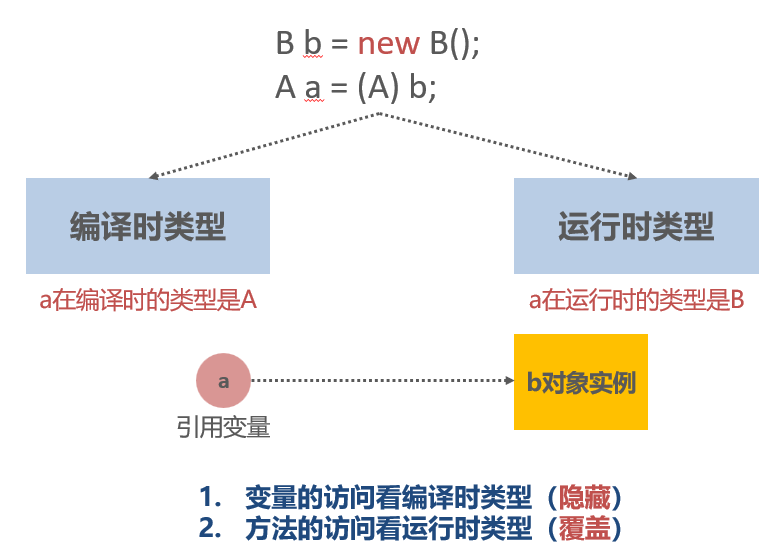

变量只会被隐藏,但是不会被覆盖。

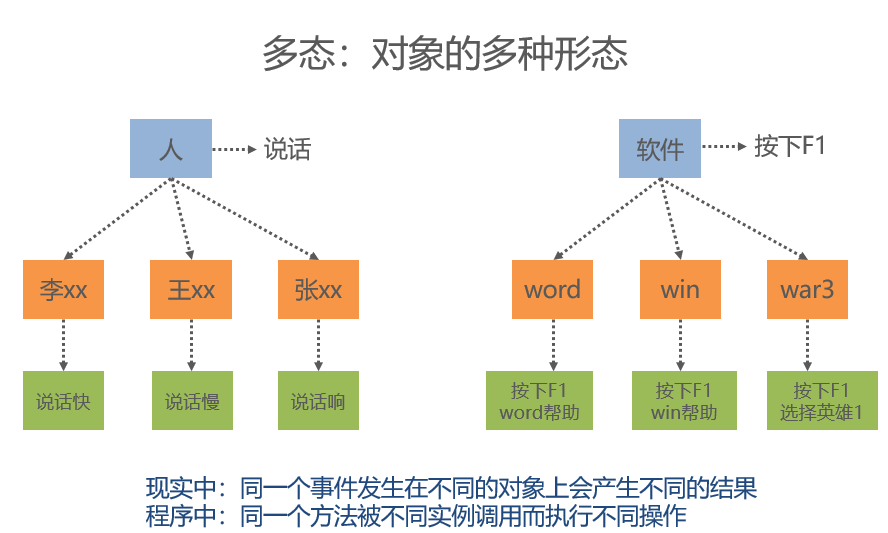
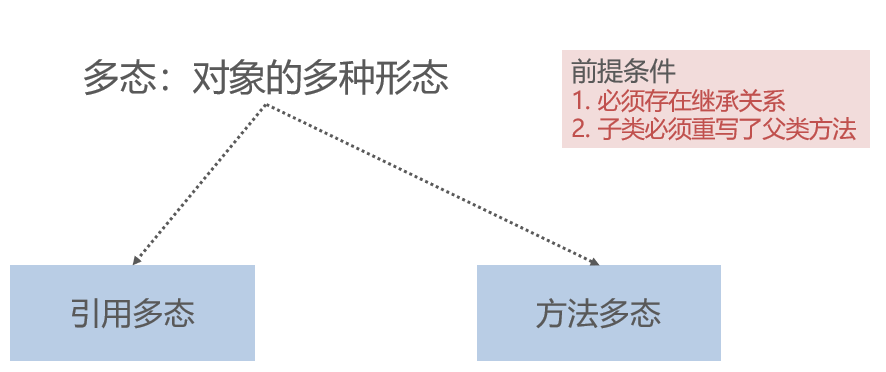
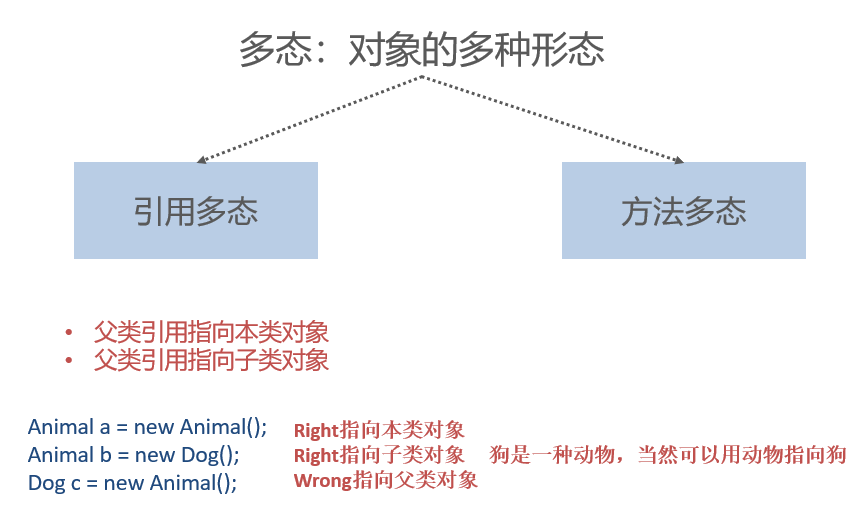
Polymorphism
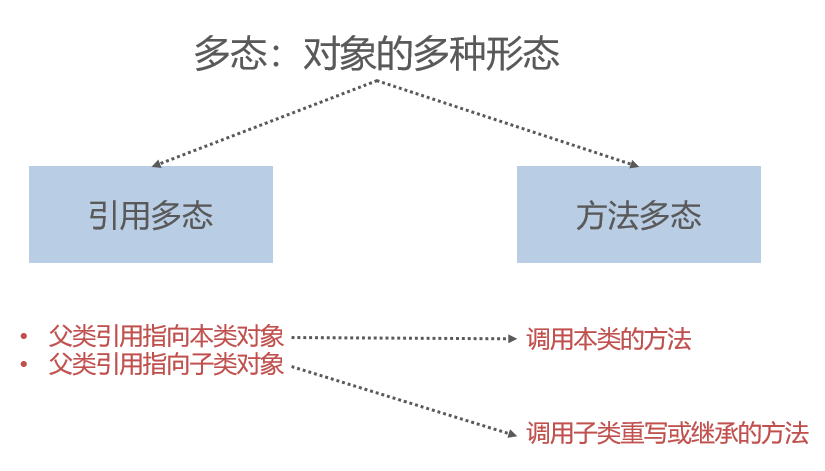

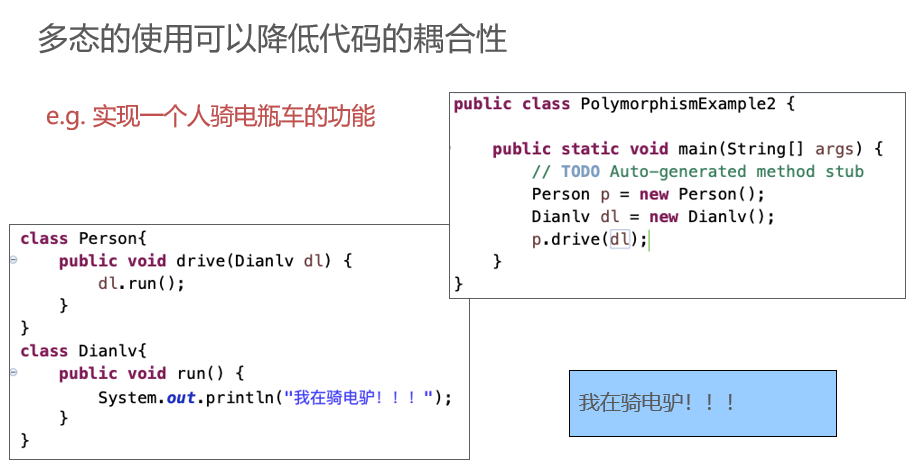

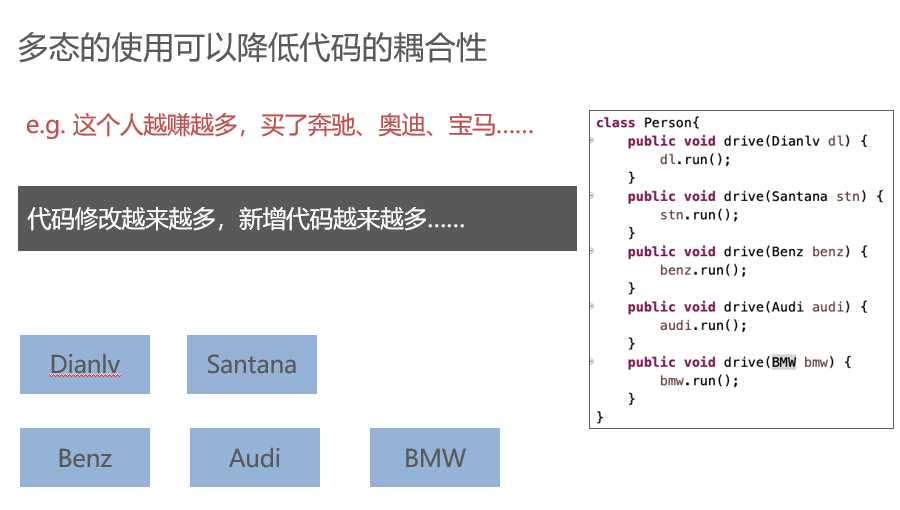
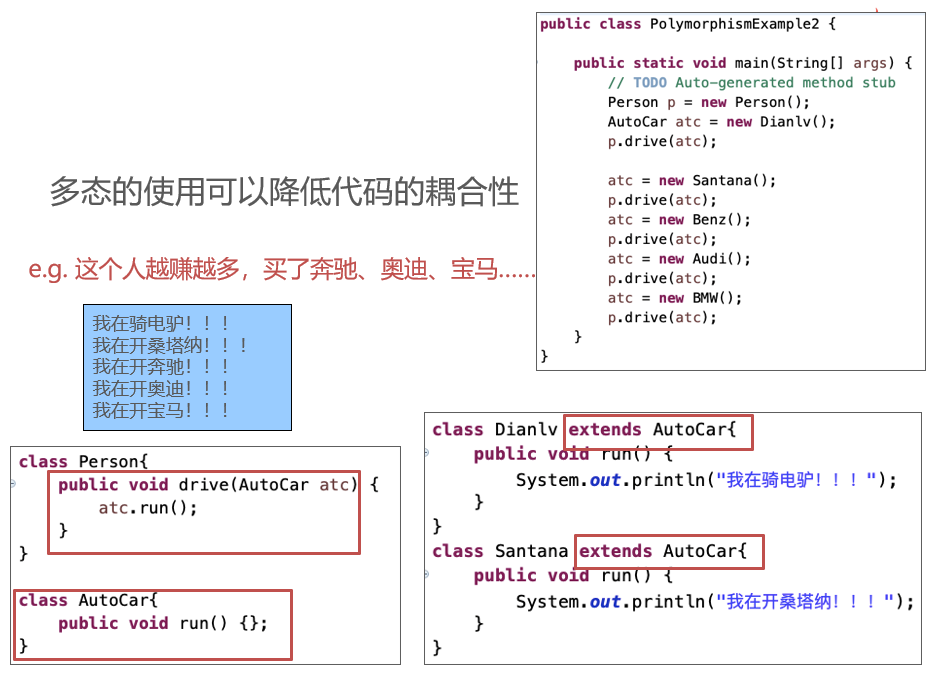
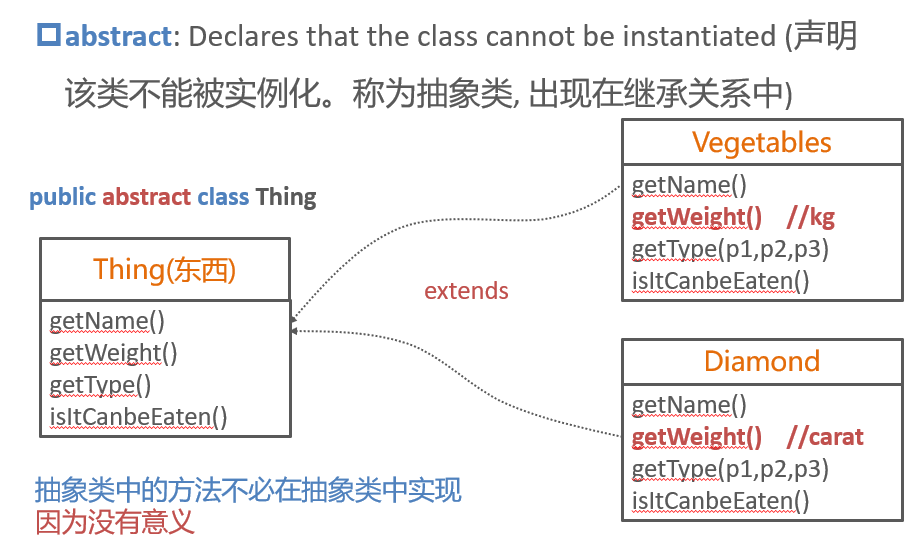
Abstract class


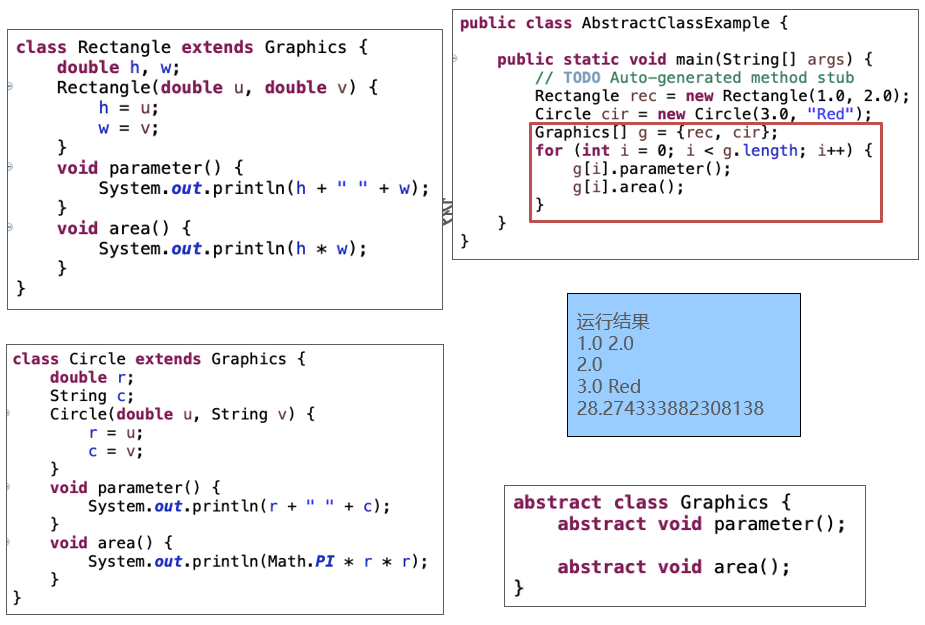
Interface
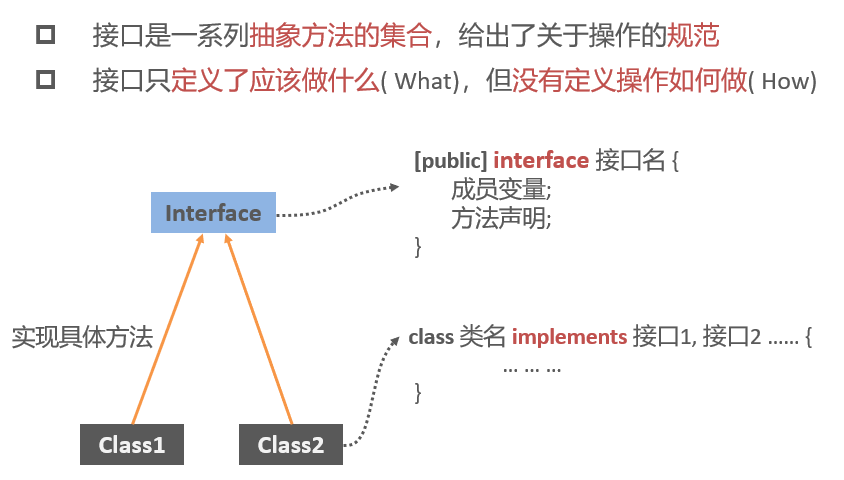
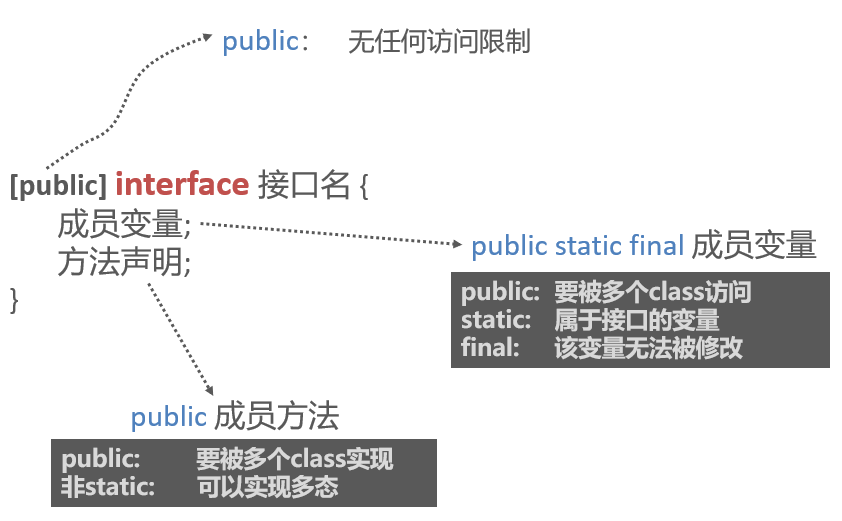
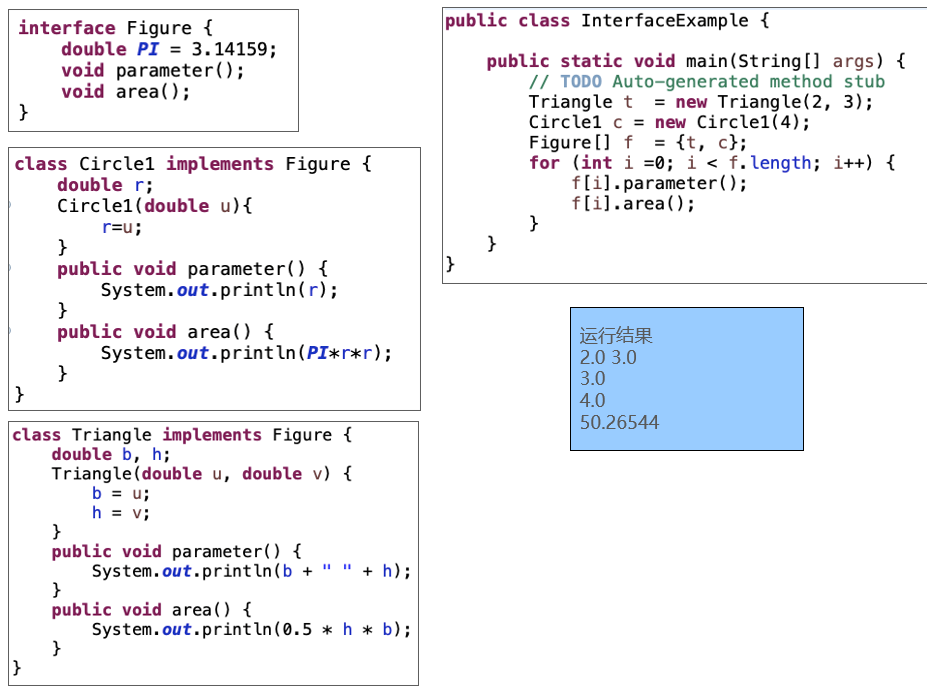
Interface inheritance
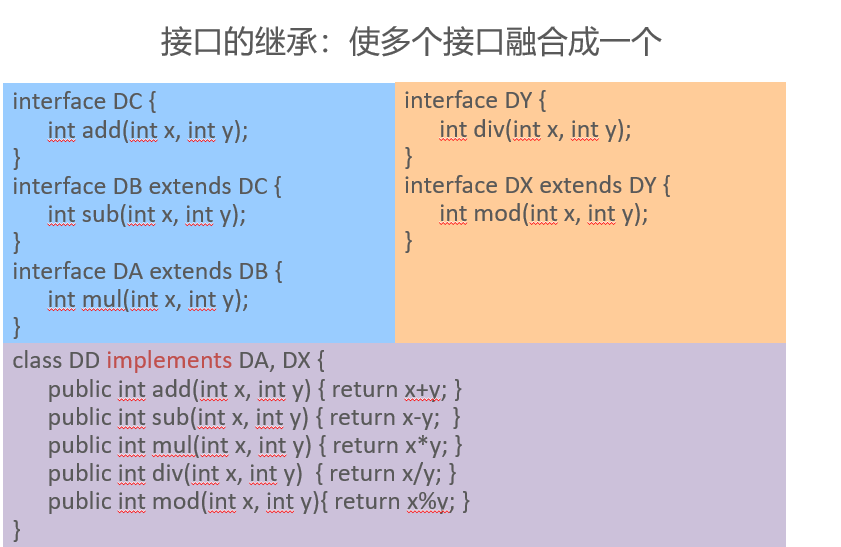
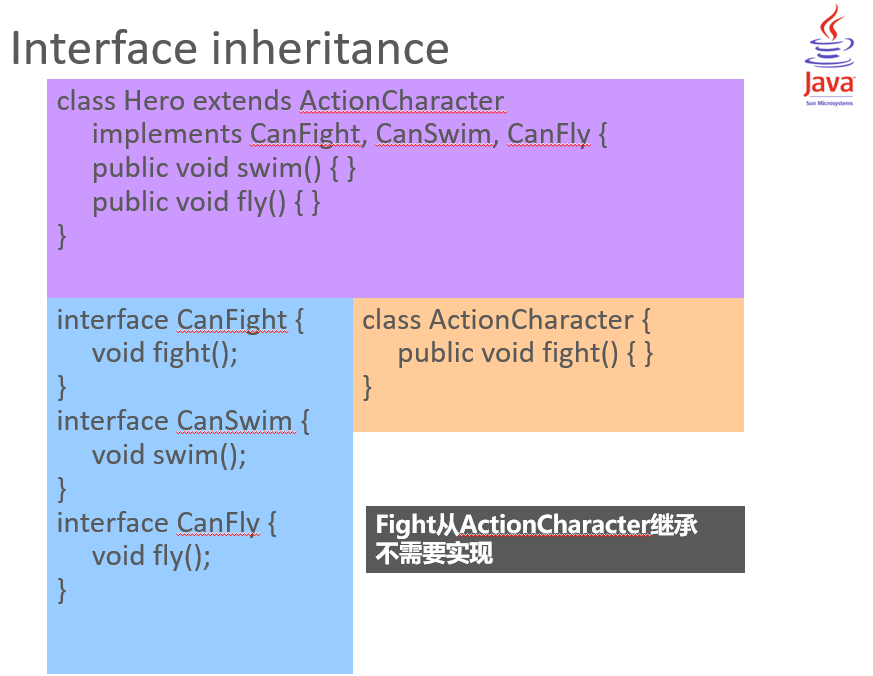
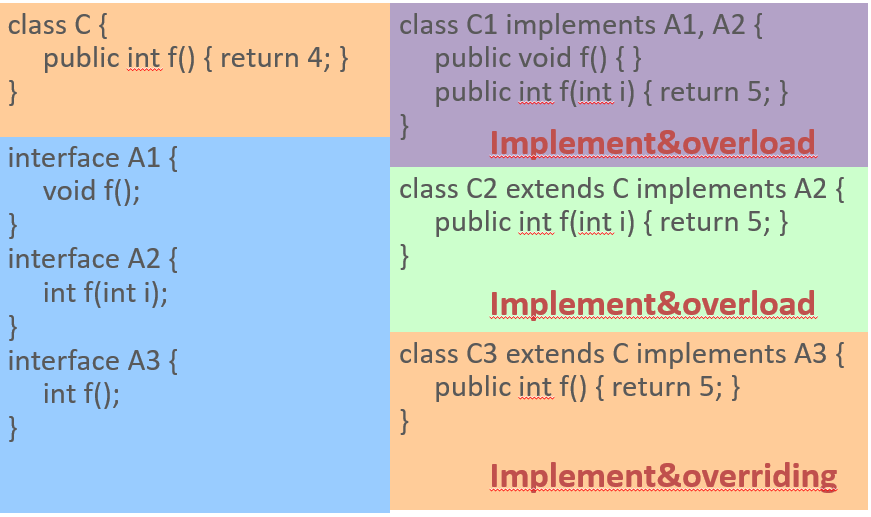
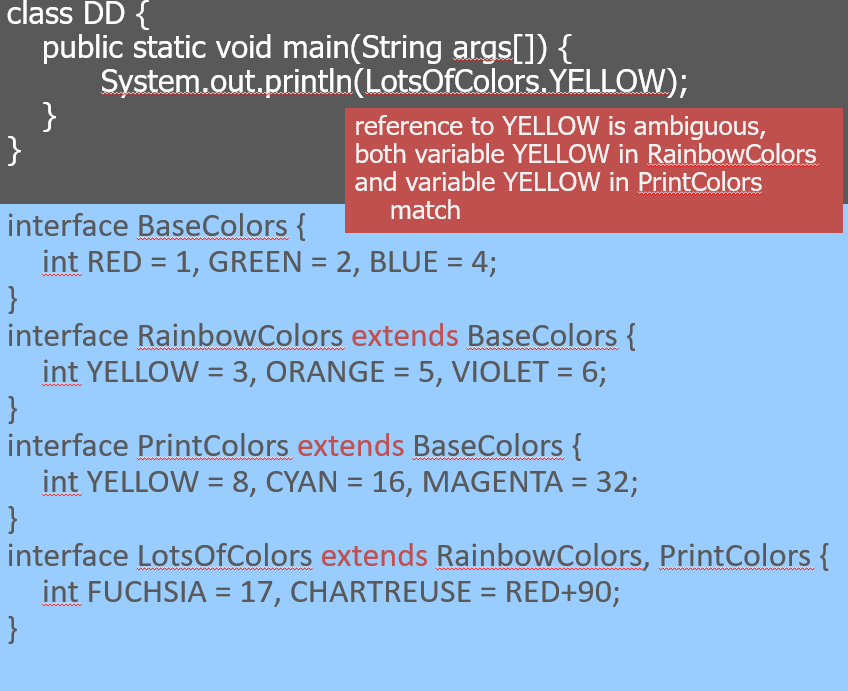
Abstract class VS. Interface
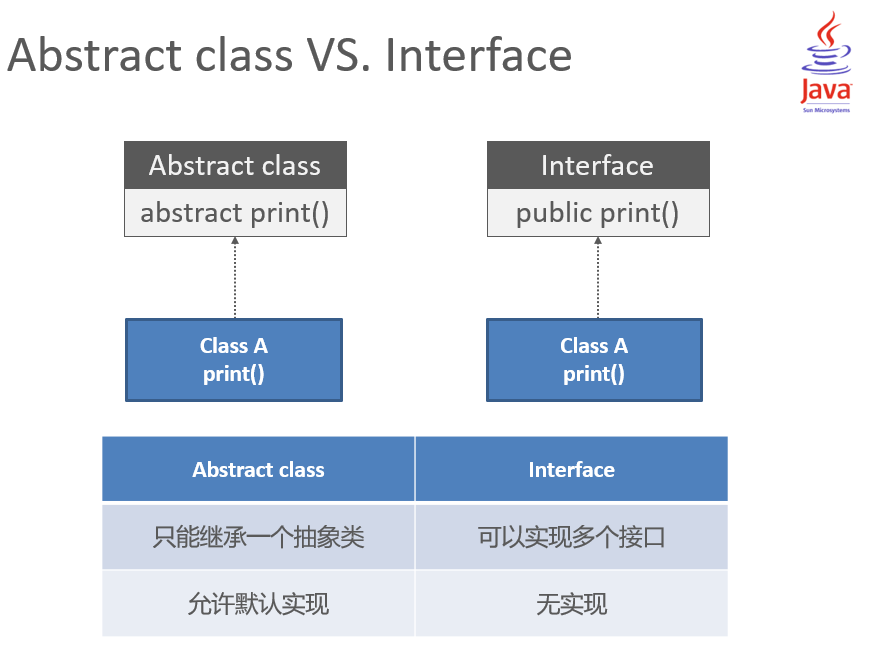
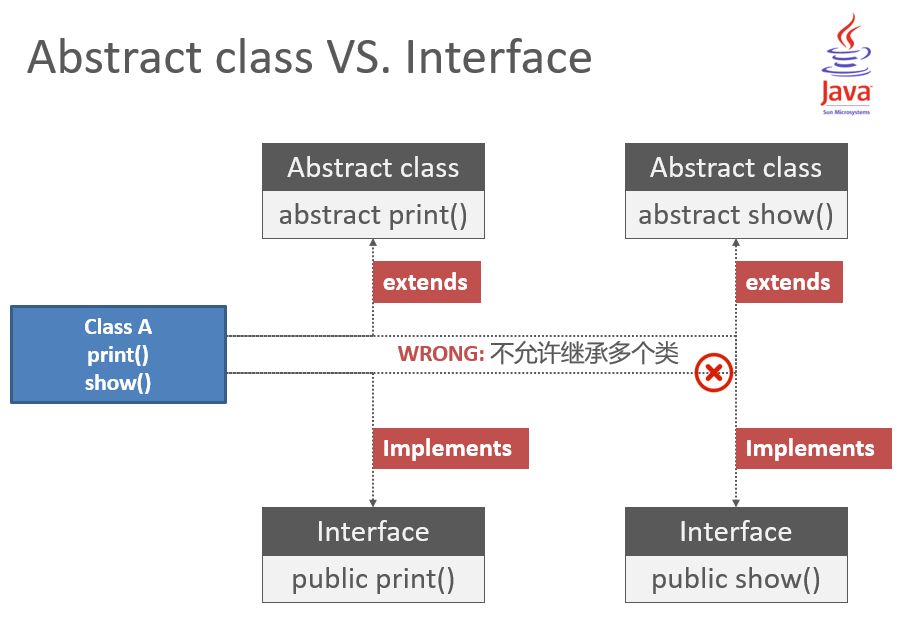
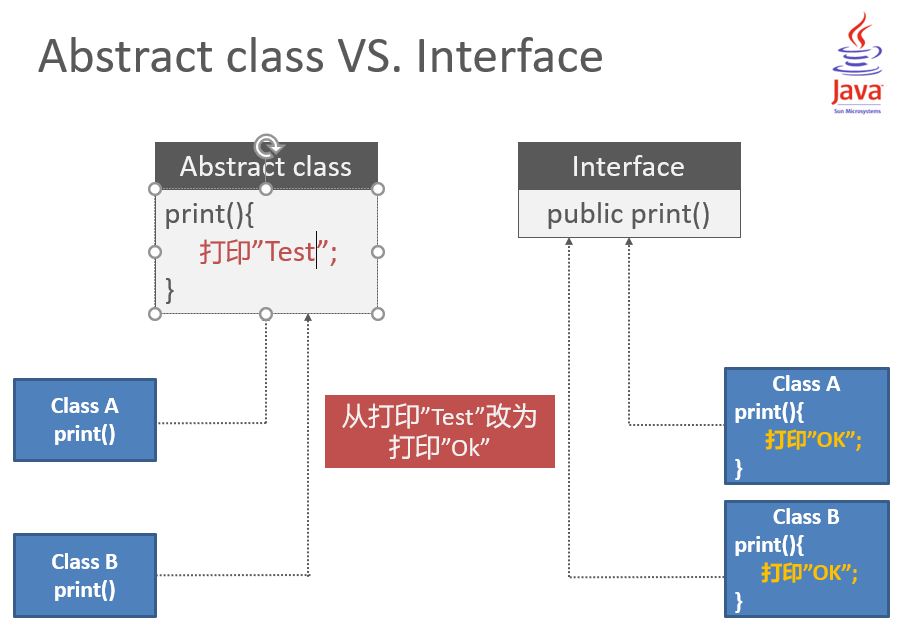
Encapsulation

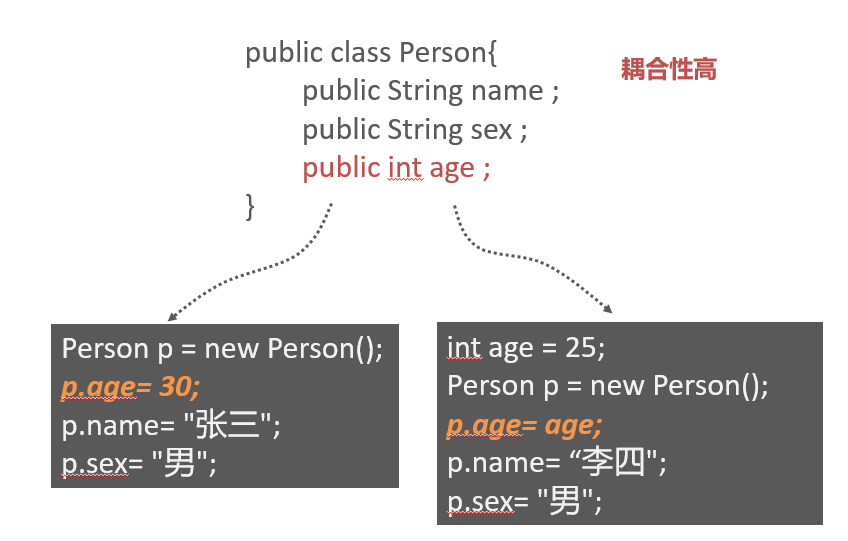
public class Person{
public String name ;
public String sex ;
public int age ;
} Person p = new Person();
p.age= 30;
p.name= "张三";
p.sex= "男"; int age = 25;
Person p = new Person();
p.age= age;
p.name= “李四";
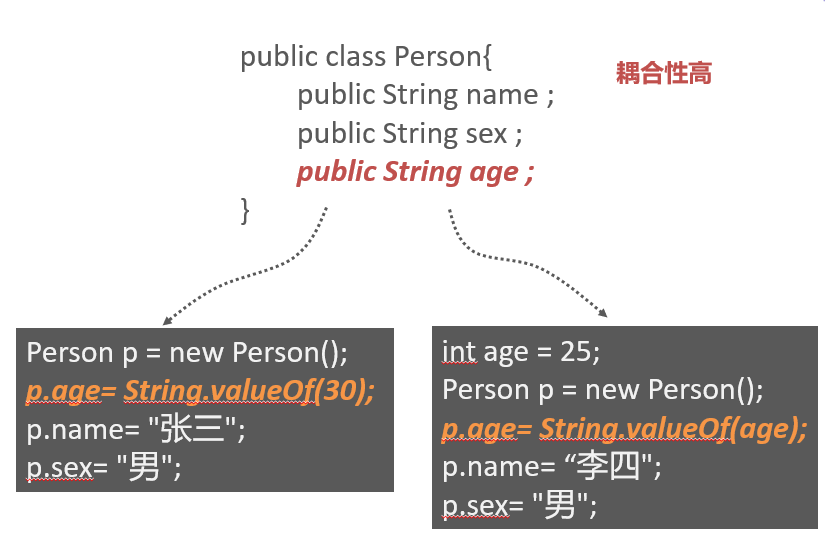
p.sex= "男"; public class Person{
public String name ;
public String sex ;
public String age ;
} Person p = new Person();
p.age= String.valueOf(30);
p.name= "张三";
p.sex= "男"; int age = 25;
Person p = new Person();
p.age= String.valueOf(age);
p.name= “李四";
p.sex= "男"; public class Person{
public String name ;
public String sex ;
private int age ;
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
} Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(20);
p.name= "张三";
p.sex= "男"; int age = 25;
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(age);
p.name= “李四";
p.sex= "男"; public class Person{
public String name ;
public String sex ;
private String age ;
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = String.valueOf(age);
}
} Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(20);
p.name= "张三";
p.sex= "男"; int age = 25;
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(age);
p.name= “李四";
p.sex= "男"; 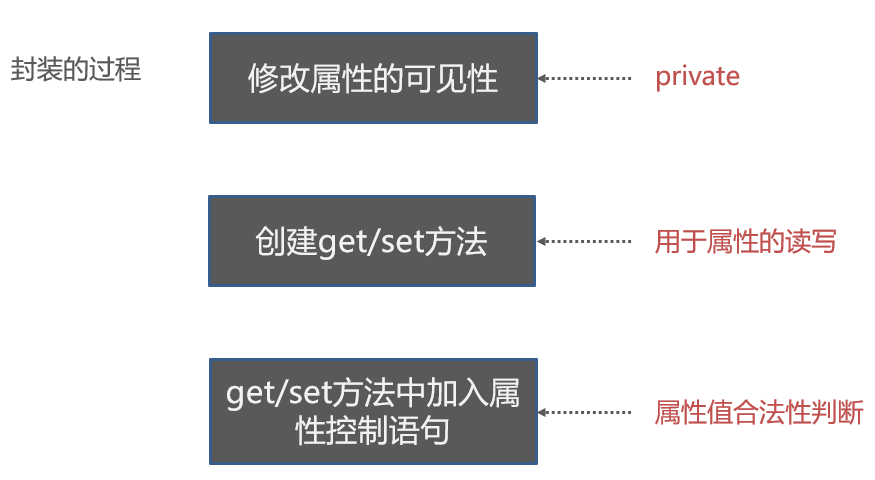
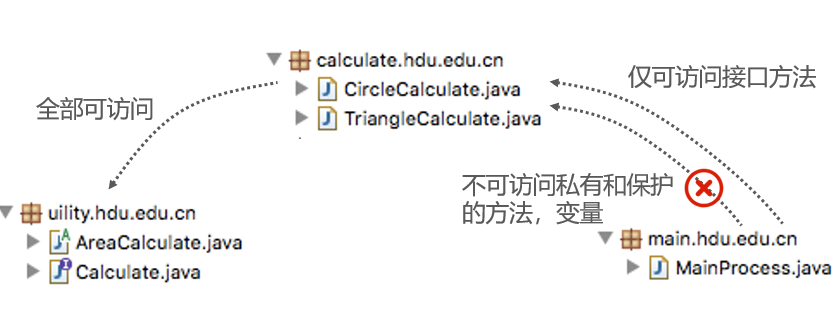
写一个多边形面积计算器,支持circle、triangle等
定义CircleCalculate类用于计算圆面积
—-extends AreaCalculate
—-implements Calculate
定义TriangleCalculate类用于计算圆面积
—-extends AreaCalculate
—-implements Calculate
Section seven
String—int的转换
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatExceptionString s = “10”;
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);String s = “10”;
int i = Integer.parseInt(s, 2);
int—String的转换

byte largestByte = Byte.MAX_VALUE;
//127 (27-1)
short largestShort = Short.MAX_VALUE;
//32767 (215-1)
int largestInteger = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//2147483647 (231-1)
long largestLong = Long.MAX_VALUE;
//9223372036854775807
float largestFloat = Float.MAX_VALUE;
//3.40282e+38
double largestDouble = Double.MAX_VALUE;
//1.79769e+308java.lang.String类
String s = new String();
char c[] = {‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’};
String s = new String(c);
char c[] = {‘语’, ‘言’};
String s = new String(c);byte b[] = {97, 98, 99};
String s = new String(b); // abc
String s = “abc”;
String s = “语言”;
String s = “”;String s1 = "java语言";
String s2 = "JavA语言";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));运行结果:
false true 32 0String s1 = "java语言";
String s2 = "java语言";
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals (s2));运行结果:
true trueString s1 = new String(“java语言”);
String s2 = new String(“java语言”);
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals (s2));运行结果:
false true
==比较值 equals比较内存地址
String s1 = "java语言";
String s2 = "JavA语言";
System.out.println(s1.length());
System.out.println(s2.length());
System.out.println(s1.substring(0, 4));
// 取出索引为4到最后的字符串
System.out.println(s1.substring(4));
System.out.println(s1.charAt(0));运行结果:
6
6
java
语言
j字符串分割: 按指定的正则表达式将字符串分割成一个字符串数组
String s = “boo:and:foo”;
String[] Result = s.split(“:”);
Regex Result
“:” { “boo”, “and”, “foo” }字符串操作类—java.lang.StringBuffer类
String s = "java语言";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(s);
buffer.append(" easy");
buffer.insert(6, " is");
s = buffer.toString();
System.out.println(s);运行结果:
java语言 is easy.
String s = “java” + “语言”;
String s = “java”.concat(“语言”);
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(“java”);
buffer.append(“语言”);
String s = buffer.toString();String str1 = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
str1 = str1 + "*";
// 383663 ms
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
sb.append("*");
String str2 = sb.toString();
// 19 ms
String str3 = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
str3.concat("*");
// 29 msint a = 1, b = 2; String c = “ men”;
String s = a + b + c;
// 3men
String s = c + b + a;
// men21字符串操作类— java.util.StringTokenizer类
字符串分割: 与String.split具有类似功能,但是做了封装
String s = "this is a test";
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
}运行结果:
this
is
a
testString s = "this:is:a:test”;
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s, “:”);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
}运行结果:
this
is
a
test// 假设有100000个tokens
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s1);
// 5ms
String[] st = s1.split(" ");
// 41msArrays class
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] a1 = new int[5];
int[] a2 = new int[5];
Arrays.fill(a1, 47);
Arrays.fill(a2, 47);
// Arrays.equals:比较两个给定的数组是否相等
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a1, a2));
a2[3]=11; a2[2]=9;
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a1, a2));
Arrays.sort(a2);
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(a2, 11));
}
}True
False
9,11,47,47,47
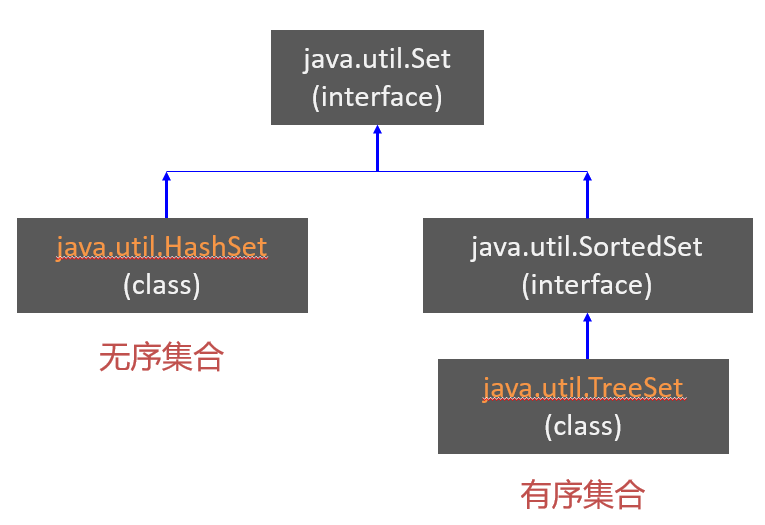
1Set interface
Set是一系列不重复元素的集合
// 用于找出文本中出现过的词
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashSet s = new HashSet();
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
s.add(args[i]);
}
System.out.println(s.size()+" distinct words: "+s);
}
}D:\java SetDemo1 i came i saw i left
4 distinct words: [left, came, saw, i]// 用HashSet找出文本中的唯一词/重复词
// 一个Set放唯一词,当无法插入该Set时意味着是重复词,则放入另一个Set
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashSet uniques = new HashSet(); //存放唯一词
HashSet dups = new HashSet(); //存放重复词
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++){
if (!uniques.add(args[i]))
dups.add(args[i]);
}
uniques.removeAll(dups);
System.out.println("Unique words: " + uniques);
System.out.println("Duplicate words: " + dups);
}
}D:\java SetDemo2 i came i saw i left
Unique words: [came, left, saw]
Duplicate words: [i]import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo4 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
boolean b;
Set s = new HashSet();
b = s.add("string1");
System.out.println("string1 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string2");
System.out.println("string2 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string3");
System.out.println("string3 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string1");
System.out.println("string1 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string2");
System.out.println("string2 add returns " + b);
Iterator i = s.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
D:\java SetDemo3
string1 add returns true
string2 add returns true
string3 add returns true
string1 add returns false
string2 add returns false
string3
string1
string2
D:\
无序输出
java.util.Iterator
迭代器(interface)
轮循
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
boolean b;
Set s = new TreeSet();
b = s.add("string1");
System.out.println("string1 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string2");
System.out.println("string2 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string3");
System.out.println("string3 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string1");
System.out.println("string1 add returns " + b);
b = s.add("string2");
System.out.println("string2 add returns " + b);
Iterator i = s.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}D:\java SetDemo3
string1 add returns true
string2 add returns true
string3 add returns true
string1 add returns false
string2 add returns false
string1
string2
string3
D:\有序输出(字典序)
HashSet VS. TreeSet


List interface
import java.util.*;
public class ListDemo1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
list.add(i + " * " + i + " = " + i * i);
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}D:\java ListDemo1
1 * 1 = 1
2 * 2 = 4
3 * 3 = 9
4 * 4 = 16
5 * 5 = 25
6 * 6 = 36
7 * 7 = 49
8 * 8 = 64
9 * 9 = 81
10 * 10 = 100Map interface

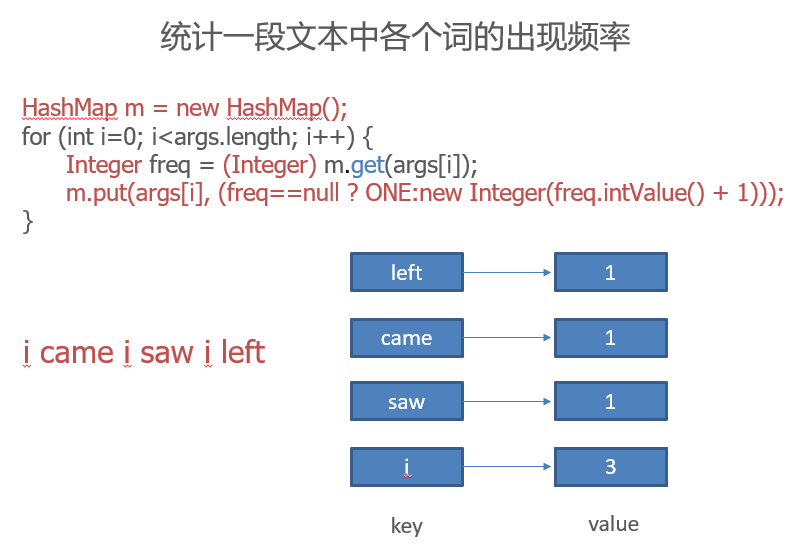
import java.util.*;
public class MapDemo1 {
private static final Integer ONE = new Integer(1);
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashMap m = new HashMap();
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++) {
Integer freq = (Integer) m.get(args[i]);
m.put(args[i], (freq==null ? ONE:new Integer(freq.intValue() + 1)));
}
System.out.println(m.size()+" distinct words detected:");
System.out.println(m);
}
}D:\java MapDemo1 if it is to be it is up to me to delegate
8 distinct words detected:
{to=3, me=1, delegate=1, it=2, is=2, if=1, be=1, up=1}用HashMap统计文档中单词的出现频率
<key, value>, key是单词,value是频率

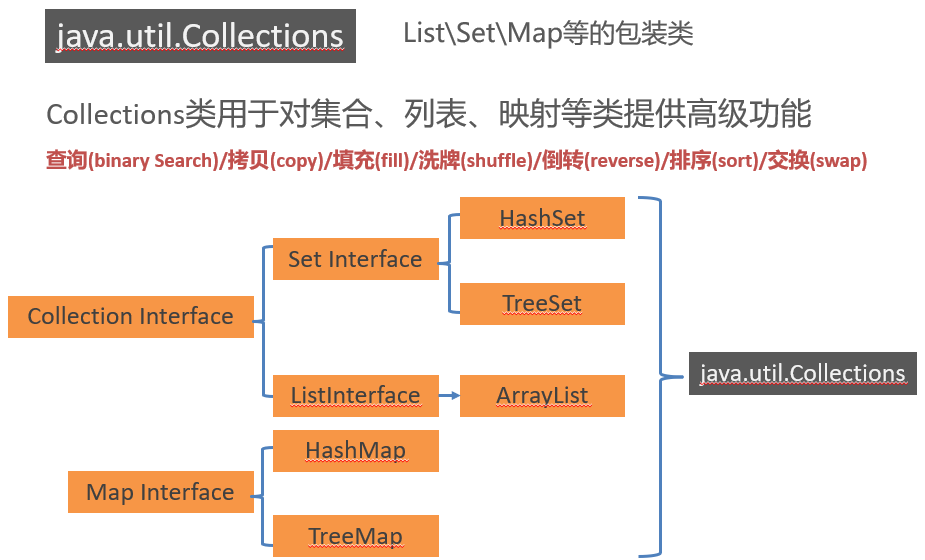
Collections class
import java.util.*;
public class SortDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(“abc”);
list.add(“DEF”);
list.add(“ghi”);
Collections.sort(list);
Iterator iter = list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext())
System.out.println(iter.next());
// 使用自定义的比较函数进行排序
Collections.sort(list, new MySort());
iter = list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext())
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}import java.util.*;
class MySort implements Comparator{
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2)
{
String s1 = (String)o1;
String s2 = (String)o2;
return s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2);
}
}可以让Collections按照自定义比较函数进行排序
Section eight
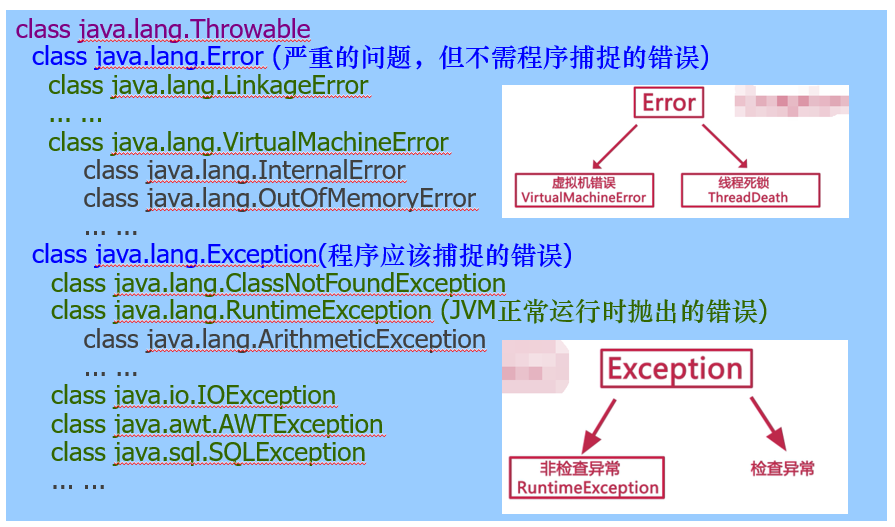
Exception
readFile {
System.out.println(“Read!”);
try {
open the file;
determine its size;
allocate that much memory;
read the file into memory;
close the file;
} catch (Exception) {
doSomething;
}
}readFile {
System.out.println(“Read!”);
open the file;
determine its size;
allocate that much memory;
read the file into memory;
close the file;
}readFile {
System.out.println(“Read!”);
try {
open the file;
determine its size;
allocate that much memory;
read the file into memory;
close the file;
} catch (fileOpenFailed) {
doSomething;
} catch (sizeDeterminationFailed) {
doSomething;
} catch (memoryAllocationFailed) {
doSomething;
} catch (readFailed) {
doSomething;
} catch (fileCloseFailed) {
doSomething;
}
}在被调用的函数抛出异常,在调用它的函数处理异常
method1 {
call method2;
}
method2 {
call method3;
}
method3 {
call readFile;
}method1 {
try {
call method2;
} catch (exception) {
doErrorProcessing;
}
}
method2 throws exception {
call method3;
}
method3 throws exception {
call readFile;
}
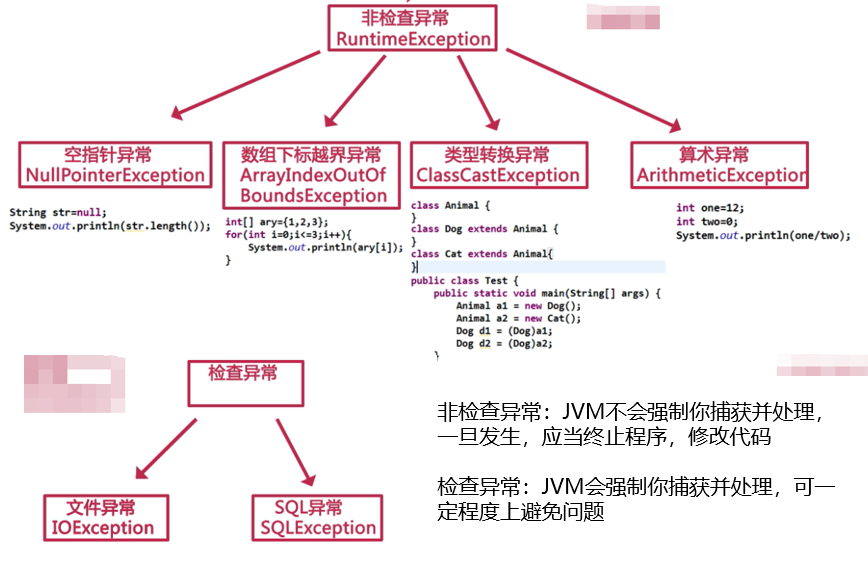
何时会产生异常?
由于非预期的结果导致系统运行时产生异常
class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0;
int b = 24/a;
}
}java Test
Exception in thread "main“
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroclass Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
System.out.println(i);
}
}java Test
Exception in thread "main“
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: “a”class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(args[5]);
System.out.println(i);
}
}java Test
Exception in thread "main“
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5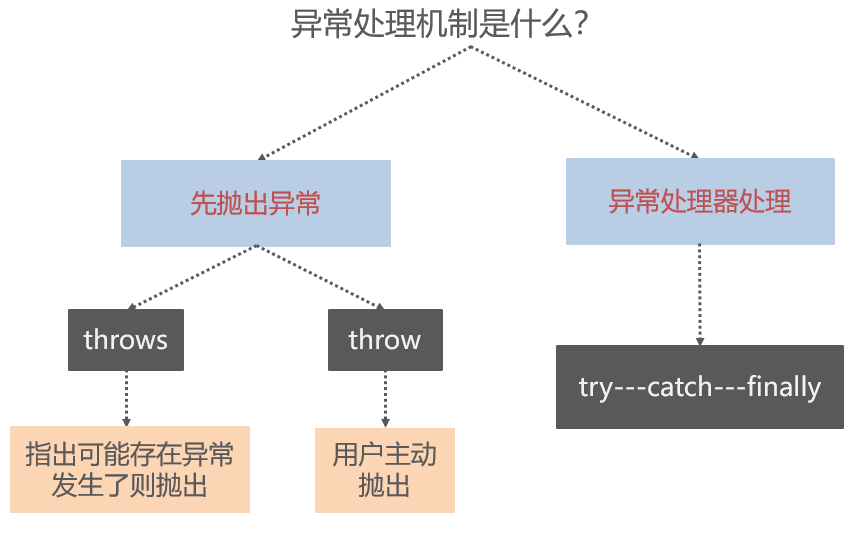
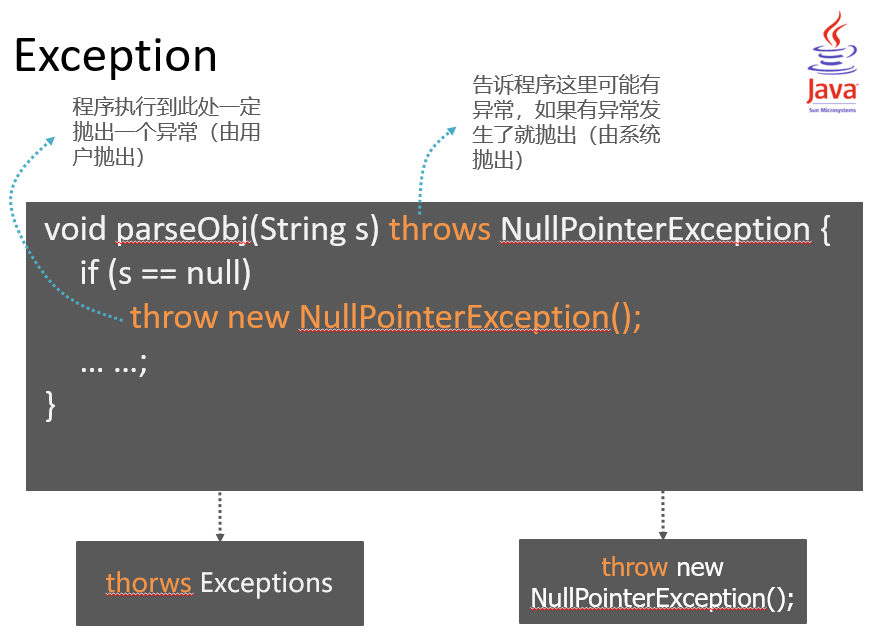
throws: 用于方法声明处,指出该方法可能发生的异常
public void function() throws NumberFormatException{
//方法体
}throw: 用于语句执行处,确定的抛出一个异常
if(s.equals("abc")) {
throw new NumberFormatException();
}异常处理器
import java.io.IOException;
class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
char c = (char)System.in.read();
System.out.println(c);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
} try–catch程序块
try {
// Code that might generate exceptions
} catch(Type1 id1) {
// Handle exceptions of Type1
} catch(Type2 id2) {
// Handle exceptions of Type2
} catch(Type3 id3) {
// Handle exceptions of Type3
}
// etc ...try {
. . .
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}try—catch—finally程序块
try {
Java 语句块; //指一个或多个抛出异常的Java语句
}
catch (Exception e) {
java语句块; //异常处理语句
}
finally {
java语句块; //善后工作
}try {
// The guarded region: Dangerous activities
// that might throw A, B, or C
} catch(A a1) {
// Handler for situation A
} catch(B b1) {
// Handler for situation B
} catch(C c1) {
// Handler for situation C
} finally {
// Activities that happen every time
}
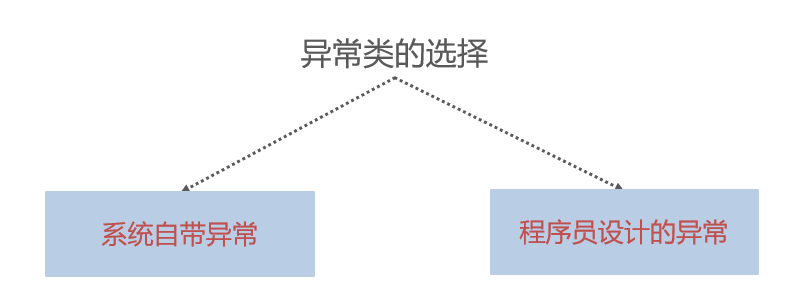

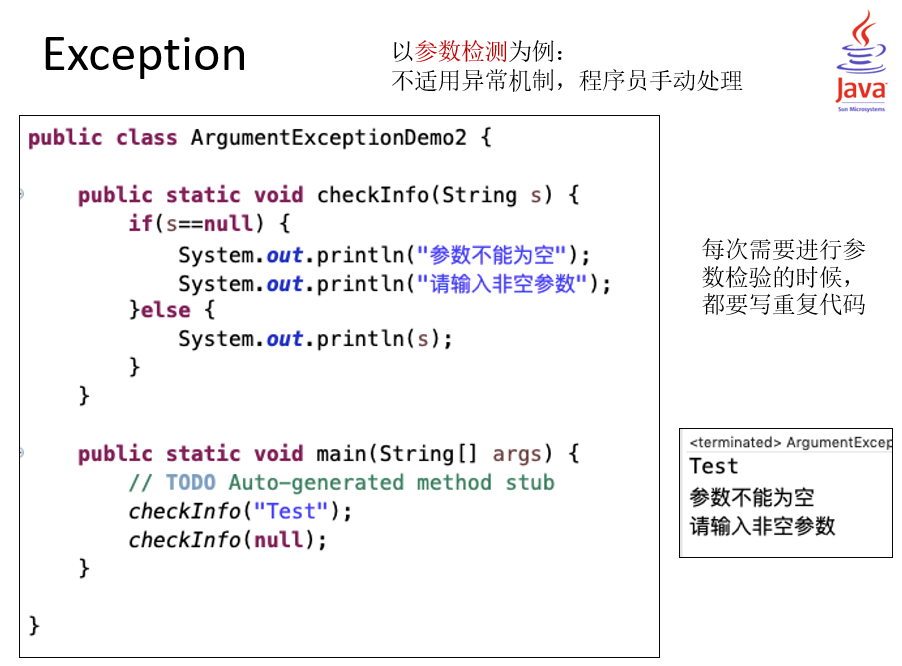
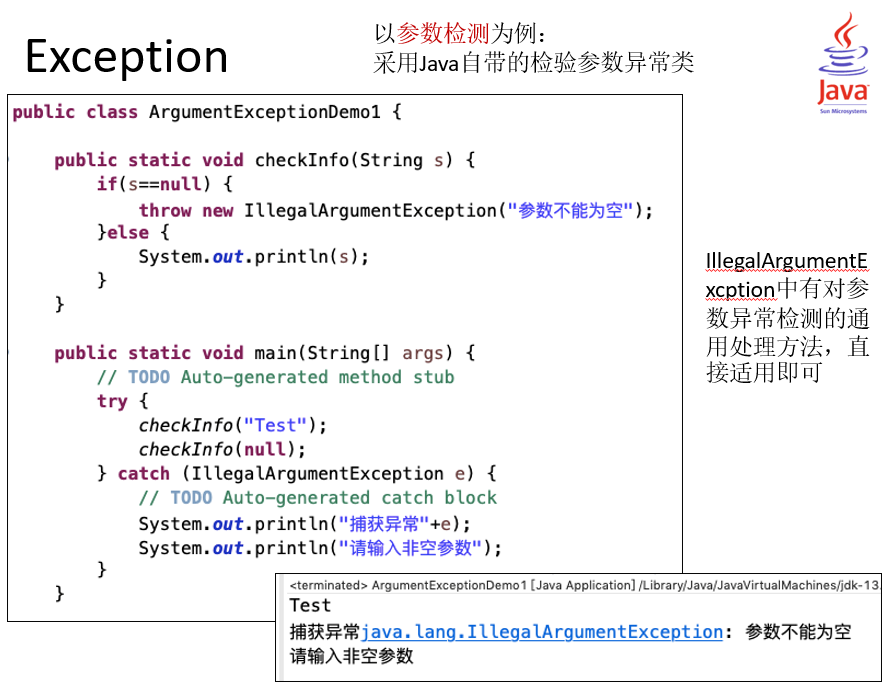

// 自定义异常
class SimpleException extends Exception {}
public class SimpleExceptionDemo {
public void f() throws SimpleException {
System.out.println("Throw SimpleException from f()");
throw new SimpleException();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleExceptionDemo sed = new SimpleExceptionDemo();
try {
sed.f();
} catch(SimpleException e) {
System.out.println(e);
System.out.println("Caught it!");
}
}
}
运行结果:
Throw SimpleException from f()
SimpleException
Caught it!



